How to Fix Magento 2 404 Not Found Errors
-
 Oleksandr Drok
Oleksandr Drok
- Administration
- Updated: Sep 12, 2025
- 17 min read
404 errors happen in every online store. That's normal. Pages appear, pages get removed, and links change.
The trouble starts when Magento 2 404 Not Found errors pile up: they waste crawl budget and chip ыaway at customer trust. A dead end breaks the shopping flow. Most visitors won't go hunting for the missing page and many simply leave. Imagine a new customer clicking an ad and landing on a 404: the content isn't there, doubts about the store grow, and the purchase never happens.
This guide shows how to find and prioritize these errors, fix the underlying causes in Magento and on the server, and when to use smart 301 redirects or the store search so people keep browsing.
Table of Contents
- Why do 404 Not Found errors occur in Magento 2
- How do 404 error pages influence the business
- How to get a list of 404 pages
- Common reasons for 404 Not Found in Magento 2
- How to resolve 404 errors
- How to create a 301 redirect
- Best pages to redirect to
- Is the design of 404 pages important
- How to make your 404 page drive revenue
- Standard Magento solution
- Can you remove a URL to fix a 404
- Conclusion
- FAQ
Why do 404 Not Found errors occur in Magento 2
A 404 Not Found error happens when the server can't find the requested URL, usually because the page was deleted, moved without a redirect, or the link is wrong. Here are the most common reasons this happens in Magento 2 and why you might see it.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, the reason for a 404 error is a change in products' or categories' URL Keys.
Also, it often happens that a store includes an extension in its functionality that changes the URL structure (for example, Layered Navigation with friendly URLs). Needless to say, this type of extension update or removal can lead to a 404 error.
And last but not least is the following reason for error: a store was migrated to Magento 2 from another e-commerce platform (Prestashop, Shopify, Drupal, WooCommerce, etc) or from Magento 1. In this case, the search systems contain thousands (if not millions) of pages with old URLs, and when trying to re-index, they end up obtaining a 404 error in response.
404s can also stem from configuration issues: an incorrect document root that does not point to /pub, disabled or misconfigured web server rewrites and .htaccess rules, missing Nginx includes, invalid Base URLs after migration or staging, or DNS and cache problems that break existing links.
On their own, 404s don't hurt rankings. When there are many, they waste crawl time and push visitors away. Keep an eye on "Not found (404)" in Search Console, and fix the root cause: add a 301 to a relevant page, or correct the server, Magento, and URL rewrite settings.
How do 404 error pages influence the business
Google's Search Central documentation notes that 404 Not Found responses are normal and, by themselves, aren't a direct negative ranking factor; newly encountered 404s are simply removed from processing and crawled less over time.
At scale, however, many "not found" URLs (and especially soft 404s) waste crawl budget, so Google recommends eliminating soft 404s and returning proper 404/410 for removed pages.
The existence of these pages themselves does not damage the website's ranking. Search engines don't lower the ranking of it if they notice a 404 error page not found.
So, should you just let them go because they pose no SEO threat? No, you shouldn't. Pages returning ‘Not Found' may not directly harm SEO, but they are still bad to have on any website.
The answer lies in the realm of UX. Statistics say that nearly 90% of users will never return to a website that gave them a bad time. Stumbling across 404 pages is not pleasant. It's like hitting a dead end and needing to start a content search all over again. Visitors do not tolerate such mistakes.
People often read repeated "page not found" messages as a sign the store is unreliable or poorly maintained, which erodes trust and hurts conversions. Clear, helpful error handling is a usability best practice for reducing frustration and keeping users engaged.
Moreover, broken backlinks can reduce traffic. If paid, email, or social campaigns point to removed URLs, you also lose that referral traffic and budget.
Speaking shortly: 404 error pages are generally not great for any business because of poor UX and broken website structure, lost referral traffic, and wasted crawl resources.
How to get a list of 404 pages
Before fixing anything, start with an inventory of all 404 pages. This section covers the main sources: Google Search Console and Google Analytics 4, and then adds other reliable ways to find 404s, including server and CDN logs, site crawlers, and campaign link checks. The goal is a complete list you can sort by impact and use to plan redirects or technical fixes.
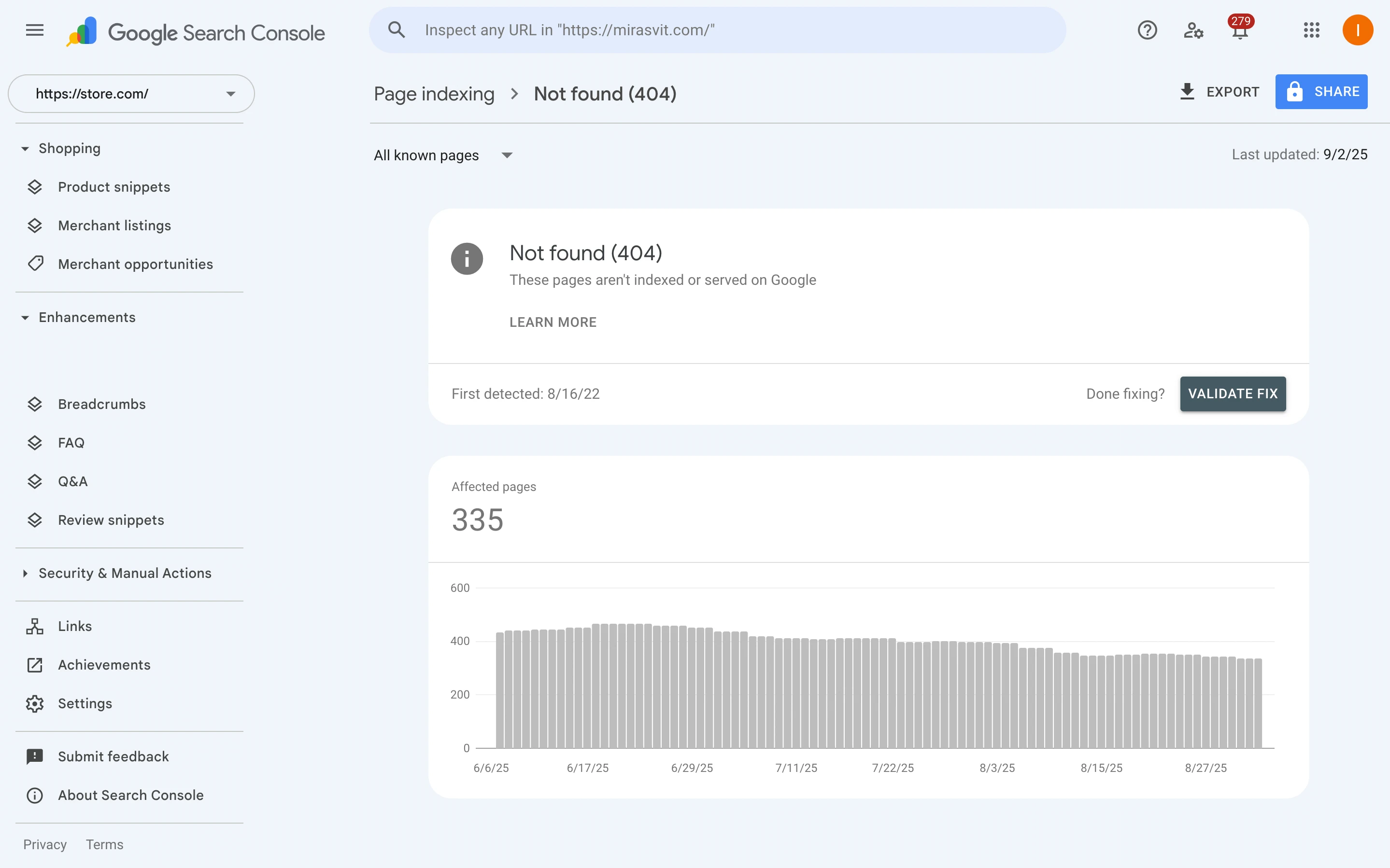
Get 404 pages from Google Search Console
Just open Google Search Console and visit Indexing > Pages > Not found (404). From there, you can export the list to CSV for processing. You can also open Crawl stats to see how often Google encounters 404s on your site.
Get 404 pages from Google Analytics
In Google Analytics, you can filter your pages using "404" in the page title; see the screenshot below.
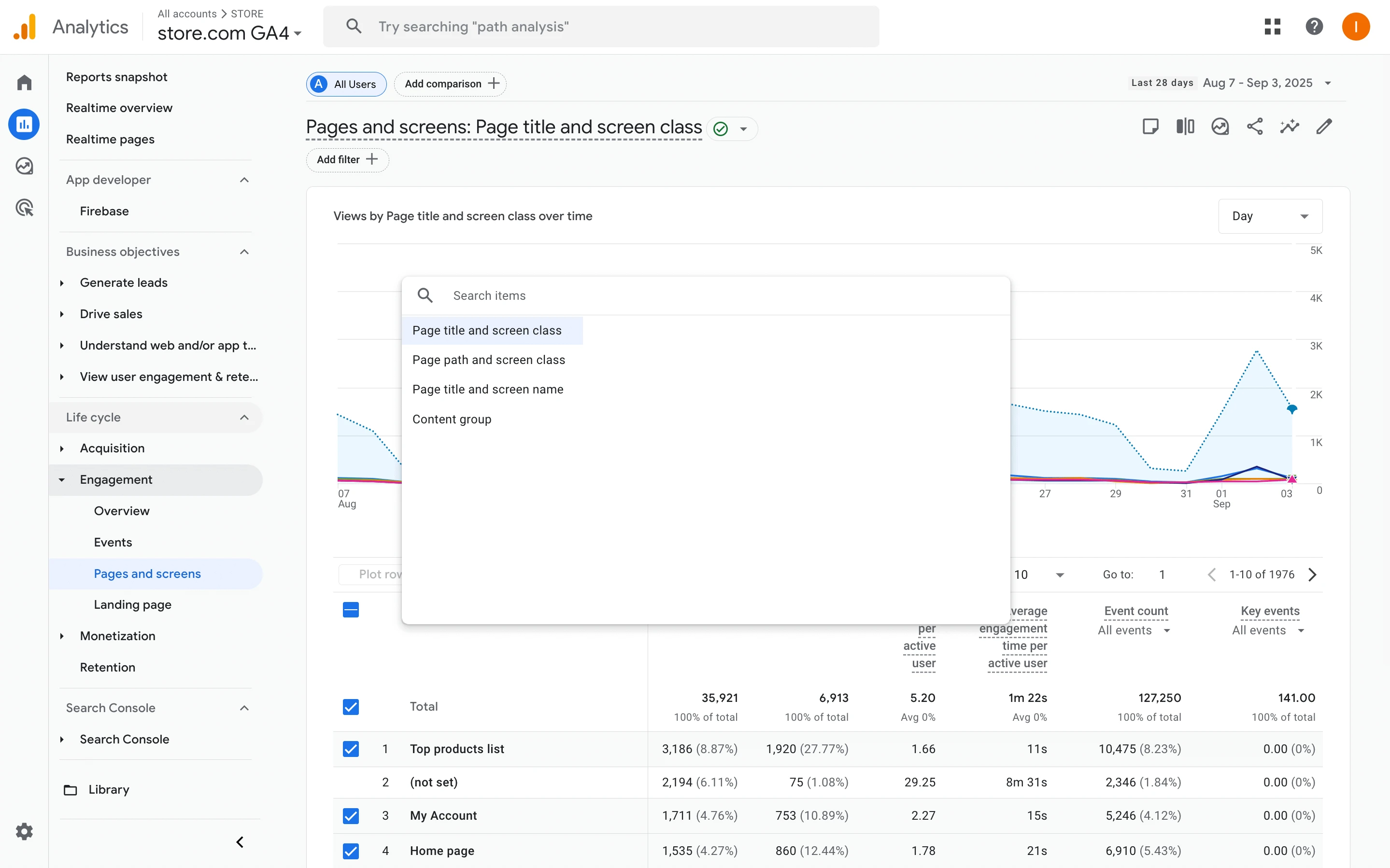
Open Reports > Engagement > Pages and screens, add a filter where Page title contains "404," or trigger a custom event when the 404 template loads. Then analyze sources in Explore or export to BigQuery to see which campaigns or referrers led users to these URLs.
Other ways to collect 404 URLs
For a complete view, add one or more of the following methods alongside Search Console and GA4.
| Method | Where to look / tool | What you get |
|---|---|---|
| Bing Webmaster Tools | Index coverage or crawl error reports | An additional list of 404 URLs beyond Google |
| Server logs | Nginx or Apache access logs | A complete list of 404 requests with counts and referrers |
| CDN or edge logs | Cloudflare, Fastly, Akamai logs or Logpush | 404s served at the edge, including cached or filtered requests |
| Site crawlers | Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, Ahrefs Site Audit, Semrush Site Audit | Broken internal and external links, plus the source pages |
| Link checkers | Dr. Link Check, Semrush Backlink Audit, Integrity | External and internal 404s, including outdated backlinks |
| CMS-level logging | Magento 2 logging on the no_route action |
404s captured in the app with request URI and referrer when server logs are unavailable |
| Centralized monitoring | Elastic or OpenSearch, ClickHouse, Datadog, New Relic | Dashboards filtered by status 404 with top URLs, referrers, and user agents |
| Campaign link checks | Batch-check ad and email URLs with a script and curl -I |
Early detection of 404 targets before ads or emails go live |
Why collecting 404 URLs matters
The main reason is simple: you may not know they are there otherwise. As was said above, these pages are caused not only by deleting old content. Adding new modules or migrating to another platform can cause them.
You may lose popular pages with flowing traffic and not even know it. Important pages with high traffic should be found and restored. Also, by closely watching the statistics regarding 404-page activity, you can determine what events cause their appearance.
Regular checks also protect crawl budget, preserve referral and campaign traffic, and help you fix issues before customers notice them.
Common reasons for 404 Not Found in Magento 2
Before you start fixing links or creating redirects, review why the errors appeared. Below are common Magento causes you can check first.
- Empty request_path in url_rewrite. Magento cannot build the path, so the page returns 404. This often affects the homepage or category pages.
- Misconfigured homepage. In Stores > Configuration > General > Web, the CMS Home Page is set incorrectly, so the root URL returns 404.
- Server setup issues. Missing or corrupted
.htaccess, disabledmod_rewrite, or an incorrect document root (the site should serve from/pub) lead to 404. - Wrong admin URL. The frontName in
env.phpor values incore_config_datado not match the actual path, so the admin opens with 404. - Cache and deployment not refreshed. After installing an extension or updating Magento, cache and generated files were not cleared, or static content and DI were not rebuilt, so some pages return 404.
- Admin user roles. The role lacks access to a resource; Magento shows 404 in the admin even when the URL is correct.
- Modules that change routes. Extensions that rewrite URLs (for example, Layered Navigation with friendly URLs) can break routing and cause 404.
- After a migration. Old URLs remain in search results while rewrite mapping is incomplete or damaged; product and category pages open with 404.
- Incorrect Base URLs or HTTP/HTTPS mismatch. A domain change or missing HTTPS sends users to outdated paths that return 404.
- Broken or duplicate url_rewrite records. Corrupted or duplicate entries disrupt routing and surface 404.
How to resolve 404 errors
Well, you have a full list of 404 error pages and now you have to redirect users to new, relevant pages. There are several options available to solve this task:
- To set redirects for all pages manually
- To redirect a user to the search page
In practice, not every 404 should be redirected. If the page is supposed to exist, fix the cause first (configuration, URL rewrites, cache). When a page was removed or moved, use redirects to guide users to the closest relevant page. Below, we cover both approaches.
When a 301 redirect is the right choice (quick recap)
Use a redirect when content was deleted or moved to a new URL, or when there is a clear replacement. Avoid sending every 404 to the homepage; point users to the closest relevant page or to search.
If you manage redirects with Advanced SEO Suite, you can add single redirects or import a CSV map. This is a good option when many old URLs have direct replacements.
When the page should exist: fix the cause
Sometimes a working page returns 404 because of configuration or data issues. In these cases, fix the root cause first.
1. 404 in the admin panel after installing an extension or updates
- Causes: cache and generated files, missing .htaccess, wrong mode, incomplete deployment.
Fix: clear cache and generated content, then run:
bin/magento cache:clean bin/magento cache:flush bin/magento setup:upgradeIf in production:
bin/magento setup:di:compile bin/magento setup:static-content:deploy- Also check that web server rewrites are enabled.
2. Wrong admin URL or base configuration
- Causes: the admin path changed or the
current URLdoes not match the configuredfrontName. Fix: show the current admin URL with
bin/magento info:adminuri, or set a new one:bin/magento setup:config:set --backend-frontname="newadmin"- If you use custom admin URLs, check related records in
core_config_data.
3. 404 on product or category pages after migration or imports
- Causes: missing URL rewrites or broken rewrite records.
- Fix: reindex URLs with
bin/magento indexer:reindex catalog_url(andcategory_urlif used), review theurl_rewritetable, and restore correct redirects from old paths.
4. URL rewrite issues, including empty or wrong request_path
- Causes: empty
request_pathrows or duplicates break routing. - Fix: remove invalid rows, reindex, and flush cache. Ensure each active product and category has the correct URL key.
5. 404 related to Content Staging (Adobe Commerce)
- Cause: content was removed or a schedule expired while related staging records remain.
- Fix: review scheduled updates for the entity, remove orphaned schedules, and publish the current version again.
6. 404 on CMS pages
- Causes: the page is disabled, the URL key is wrong, or the page is not assigned to the current store view.
- Fix: open Admin > Content > Pages, ensure the page is enabled, the
URL keyis correct, and the page is assigned to the needed website and store view. - If a page is truly gone, add a 301. If the page should exist, correct the configuration or data so the URL works, then retest your list of 404s and keep only redirects that improve the user path.
How to create a 301 redirect
When a page no longer exists or was moved, create a 301 redirect to guide users to the right content.
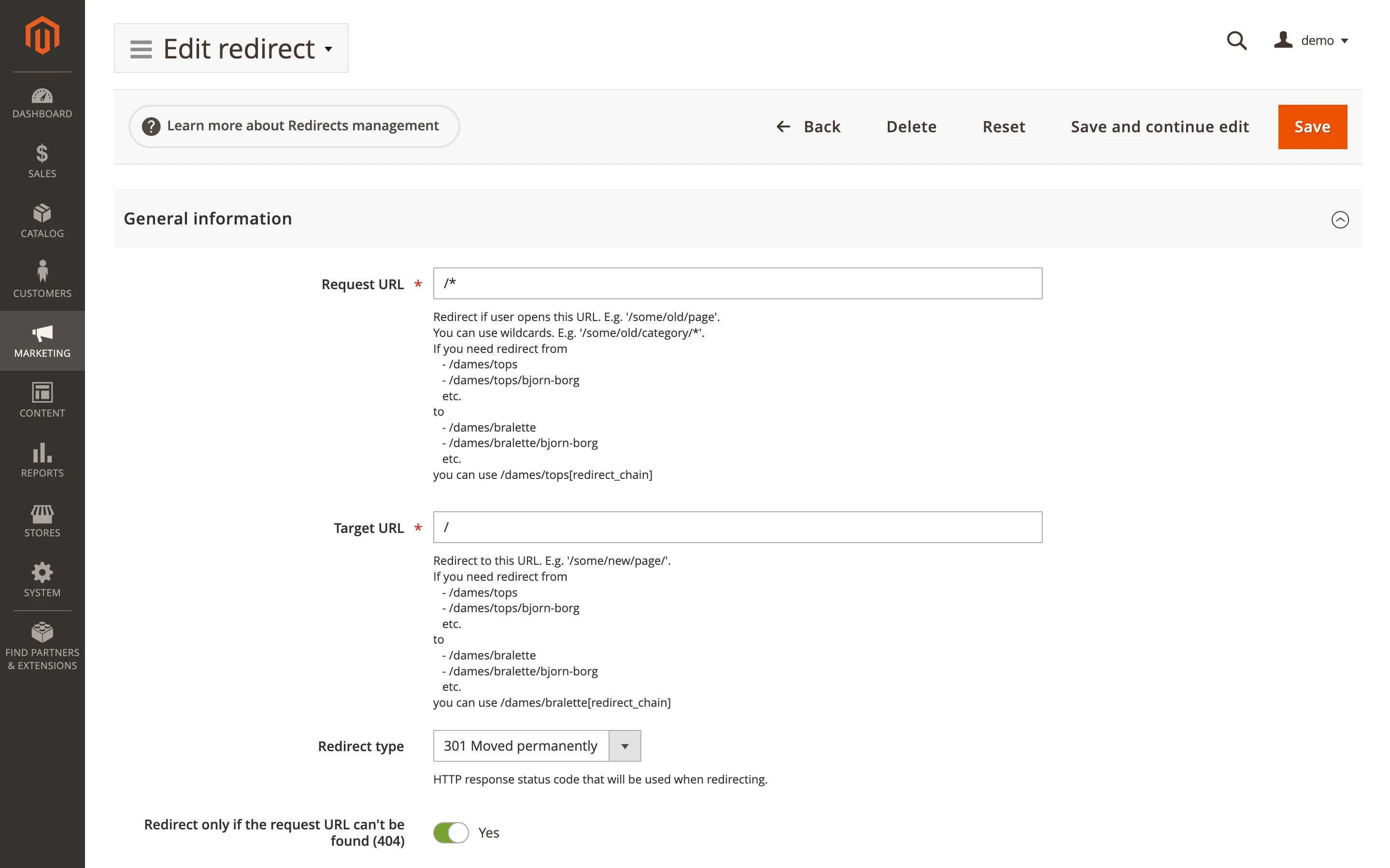
If you use Advanced SEO Suite, you can redirect users from a 404 page to a new page by simply going to Marketing > Advanced SEO Suite > Redirects and adding a redirect there:
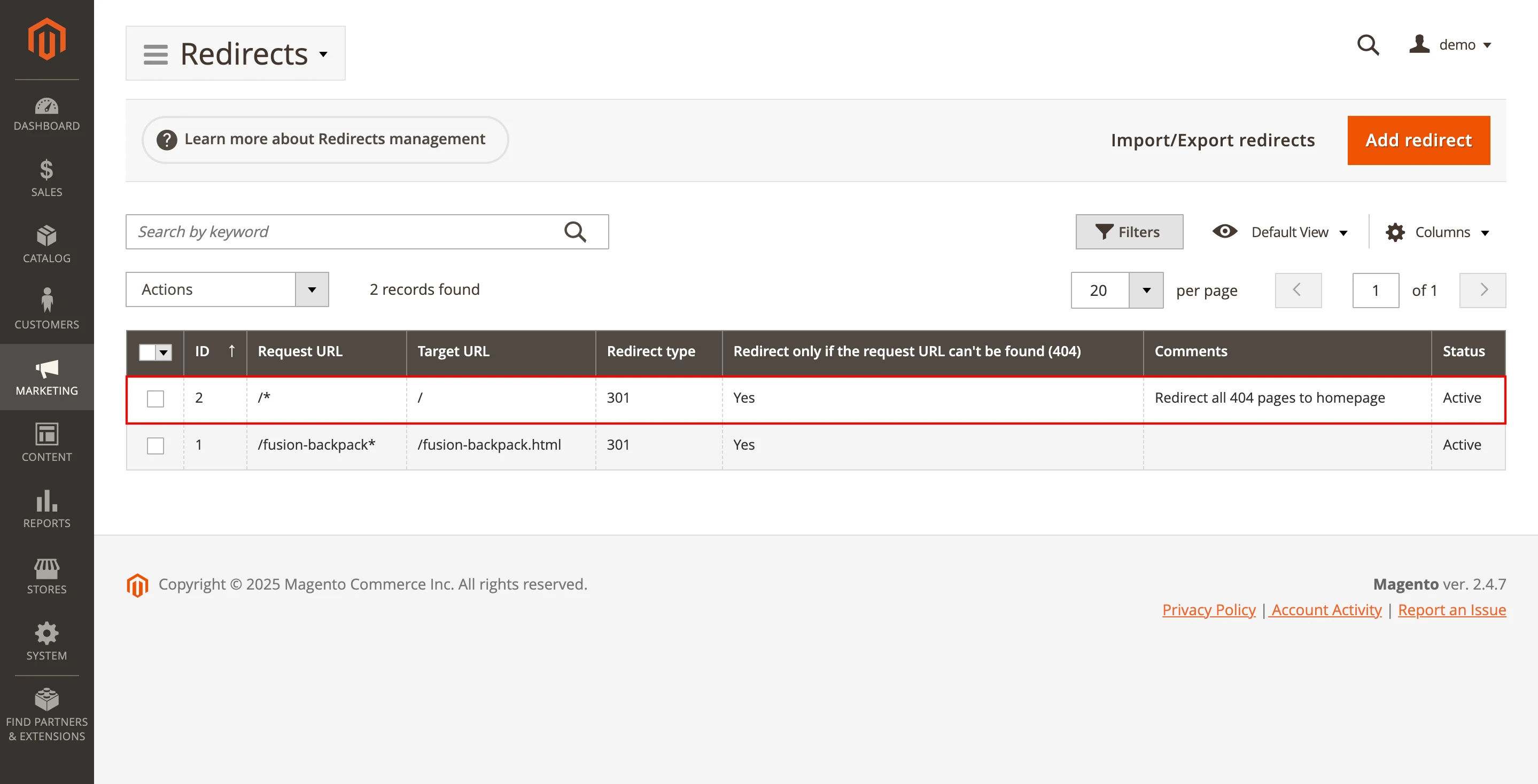
Also, you can import a .csv file with all the required redirects, using the inbuilt import option.
However, the main disadvantage of this approach is the necessity to create a list with matching old and new URLs. If you have more than 1000 pages, it is much faster to set a redirect to the search page, which will ensure that you cover all 404 pages.
Tip: after adding redirects or importing a CSV, clear the cache and test a sample of URLs to confirm the target pages open as expected. Avoid blanket redirects to the homepage. Map top legacy URLs to the most relevant categories, products, or content, or use search when there is no one-to-one match.
Best pages to redirect to
There are enough options for custom redirects for 404 error, but what are the best ones? There are three effective choices:
- Landing. An option that never gets old — redirect users to the landing or main page. Not the most pleasant solution, but a simple and comprehensible one. It has a reasonable chance to hook users back in, especially if the page is well-designed.
- Product list or search page. The user won't land on the exact page, but they stay in the flow and can keep searching. And if he already knew what he was here for — this option serves as an inviting crossroad for a different query.
- FAQ. If users don't land on the desired page, they will have questions. Why not address them immediately by sending users to an FAQ section of your website?
Note: Use the homepage only when it makes sense for the intent. In most cases, a category, a close alternative, or a search results page keeps the user engaged better than a generic landing.
How to redirect 404 pages to search
This option is available in our Elastic Search Ultimate and Sphinx Search Ultimate extensions for Magento 2.
To enable the option, simply go to the extension settings Store > Configuration > Mirasvit Extensions > Search and activate the Redirect 404 pages to search results option.
Now the search will automatically display relevant results for all 404 pages in accordance with the requested URL.
After enabling the option, watch your analytics. Check GA4 reports to confirm that 404 hits drop and that users continue browsing from the search results. If needed, fine-tune synonyms and stop words so results look relevant.
Is the design of 404 pages important
Many companies have special designs for 404 error pages. Users are greeted by funny robots, cute bears, or other mascots and kindly sent to a relevant page. Businesses do this to improve user comfort and make potential customers feel cared about. Sure, you can redirect people from 404 pages. But wouldn't that be nice if, before that, they saw a pleasant message?
A thoughtful 404 page helps preserve the user journey by giving a clear message and an obvious next step.
So, even if you set up redirects, it is still useful to customize your error message pages. Magento 2 extensions can help you with that. They can give you the right tools to create unique designs and draw a little chuckle from a user who stumbled upon a nonexistent page.
Practical elements also matter: add a search field, links to popular categories or help, and a short path back to the homepage. Consider a small feedback form so users can report a broken link. These touches can lower bounce rates, keep visitors browsing, and protect conversions.
In short, the design of a 404 page affects retention and trust. A clear message and useful navigation reduce frustration and keep users on the site. Thoughtful styling supports your brand and leaves a positive impression. Links to relevant sections and built-in search help people recover quickly. A simple feedback option turns an error into a helpful touchpoint.
How to make your 404 page drive revenue
The answer is simple: customize them to be entertaining or promotional. In the first case, you can build trust and boost interest by making an error 404 page engaging. Write trivia there and add art. This way, instead of broken pages, you will have more content for your users.
In the second case, you may add an advertisement to a 404 page. Search engines won't be interested, but your users might be. So how can you do it?
Here are practical ideas that turn a 404 into a conversion point:
- Promotions and special offers. Show a small banner or a promo block with a discount or coupon so visitors have a reason to keep shopping.
- Product recommendations. Replace "Page not found" with a short grid of popular items or top categories.
- Built-in search and quick links. Add a search field and shortcuts like "Bestsellers," "New arrivals," or "Sale."
- Partner or house ads. On high-traffic stores, use the space for partner banners or your own seasonal campaigns.
- Branding and trust. Keep the tone friendly and on-brand so people feel guided rather than stuck.
Standard Magento solution
Basic Magento 2 tools can be used to customize the 404 page. The entire process will be done through an admin panel. Open it, go to the Content menu, and then to Pages. You will see a list of all pages that make up your website.
Use the search bar in the top-left and type in proper keywords, like "404", to find the needed page. Then, you just select the "Edit" option in the drop-down menu on the right. The page's content may be rewritten in HTML and CSS.
On this page, place a search widget, links to key categories, and a small promo banner. Track clicks with your analytics to see which blocks help people return to browsing.
Can you remove a URL to fix a 404
Short answer: no. It is important to choose the right way how to fix a 404 error. While you technically can put content somewhere else or delete it entirely, it would not resolve the problem. Say some other website referred to you in their blog or article. If you place the same content under another URL, that link will still be broken. Third-party websites probably won't update it. Moreover, even internal linking can be destroyed by rash changes.
The better approach is to fix the link path, not hide the symptom:
- Correct broken links where possible (update internal links and campaign URLs).
- Set 301 redirects from removed or changed pages to the closest relevant content (category, product, or an informative alternative).
- If a page is permanently gone and has no equivalent, let it return 404 (or 410). Remove it from sitemaps and internal navigation so search engines drop it naturally.
Bottom line: don't "solve" a 404 by deleting the URL. Either fix the link or map a 301 to a suitable page. If there's no replacement, keep the 404 and clean up references so users and crawlers don't keep hitting it.
Conclusion
404 errors are routine in online stores; eliminating them completely is costly and unnecessary. The pragmatic route is to find them regularly, decide whether the page should exist, then either fix the cause or map a 301 to a relevant alternative.
Use Search Console and Google Analytics to prioritize and rely on redirects only where they help. A helpful 404 page with search and clear links reduces frustration and keeps visitors browsing. When managed this way, 404 Not Found pages don't derail rankings or conversions in Magento 2; they are small course corrections, not big problems.
FAQ
How do I fix a 404 Not Found error in Magento 2?
To fix a 404 in Magento 2, first decide if the page should exist. If yes, check document root points to /pub, enable Web Server Rewrites, verify Base URLs, reindex URL rewrites, and clear cache and static assets. If the page was removed or moved, add a 301 redirect to the closest relevant page or to search when there is no one-to-one match.
How do I find 404 pages on my site?
To find 404s, use Google Search Console under Indexing → Pages → Not found (404), and in GA4 filter Pages and Screens by a page title containing "404" or trigger a custom 404 event. For a full list, review server or CDN logs and run a site crawl to locate broken internal and external links.
What is the most common cause of a 404 in Magento 2?
The most common cause of a 404 in Magento 2 is changed or missing URL keys and rewrites for products or categories, especially after migrations or bulk edits. A close second is broken or duplicate entries in the url_rewrite table.
Is a 404 bad for SEO?
A single 404 is not a direct negative ranking factor, but many 404s waste crawl budget and create a poor user experience. If content is gone for good, return 404 or 410; if it has a replacement, use a 301 redirect rather than sending everyone to the homepage.
How can I prevent new 404 errors?
To prevent 404s, keep URL rewrite mappings up to date when changing URLs, ship a redirects CSV with releases, and QA internal links and sitemaps. Monitor GSC and GA4 regularly, watch server or CDN logs for spikes, and test campaign and email links before launch.
From meta tags to the sitemap, the Magento 2 SEO Extension gives you full control over each and every SEO-related feature in your store.
This extension is a SEO powerhouse that provides major enhancements to all pages of any online shop.
This amazing package will save you an incredible amount of time and money, all while securing your site's place at the top of the search results!
A well-designed blazing fast search in a store will increase its conversion rate and revenue growth.
The Elasticsearch extension provides a multifunctional in-store search system that returns relevant results within milliseconds.
Provide great search results to your customers, and give them incredible experience, so that they could find and buy items they want much easier.





