Magento vs WordPress: A Complete eCommerce CMS Comparison
-
 Oleksandra Petrenko
Oleksandra Petrenko
- Magento 2
- 9 min read
Selecting a suitable Content Management System (CMS) can define the success of your commercial project. These platforms enable you to build your digital storefront and promote products or services. With numerous options in today’s market, Magento and WordPress stand out as two prominent choices, each offering a specific toolset.
In this article, we will compare Magento and WordPress, exploring their key attributes, target audiences, and the advantages and disadvantages they bring to the table. By understanding the fundamental distinction of these solutions, you can make informed decisions based on your current market situation and growth strategy.
Overview of Magento and WordPress
Magento, currently under Adobe's ownership, was initially created to design e-commerce stores. Its solid functionality is responsive to solving profound e-commerce challenges and issues. With features for comprehensive modulation, seamless growth, and fast performance, Magento serves a great range of enterprises from different industries. The audience includes startups and well-known brands who seek an effective online presence.
Conversely, WordPress was originally conceived as a platform for blogs. It has grown into a multitask CMS powering a large portion of websites around the globe, along with e-commerce shops. Integration with the WooCommerce plugin extends its toolset to become a whole-scale market platform by catering to a straightforward user experience, extension support, and flexibility sutitable for small and medium companies seeking cost-effective solutions.
Magento CMS
Key Features
1. Easy Adjustments: With Magento, you can easily tailor your design with easy-to-edit themes and templates to reflect the brand style and unique selling propositions. Moreover, it delivers advanced flexibility for product pages, transaction operations, and user experience.
2. Scaling: Magento suits the needs of companies of all sizes – from humble shops to large enterprises. With Magento, expanding product offerings, customer base, and sales volume over time is painless.
3. Performance Optimization: Magento prioritizes fast loading times, smooth navigation, and seamless customer checkout experiences. Native features like full-page caching, database optimization, and content delivery network (CDN) integration help enhance website performance and responsiveness.
4. Marketing and Analytics Tools: Magento helps businesses increase traffic, attract customers, and optimize their marketing strategy. From built-in SEO features and marketing automation capabilities to comprehensive analytics dashboards and reporting tools, Magento equips retailers with the insights they need to make data-driven decisions and maximize their sales potential.
Target Audience of Magento
1. Large Retailers: Magento Commerce is a solution for big companies and established brands offering administration of multiple stores from a single dashboard, advanced security options, and enterprise-level support.
2. Mid-sized Companies: Ventures seeking a powerful yet cost-effective service to build their digital storefront prefer Magento for its adaptability, easy expansion, and vast adjustment options.
3. Small Shops: Magento's free open-source code offers a rich selection of functions to build and scale online shops smoothly.
Pros and Cons of Using Magento for Ecommerce
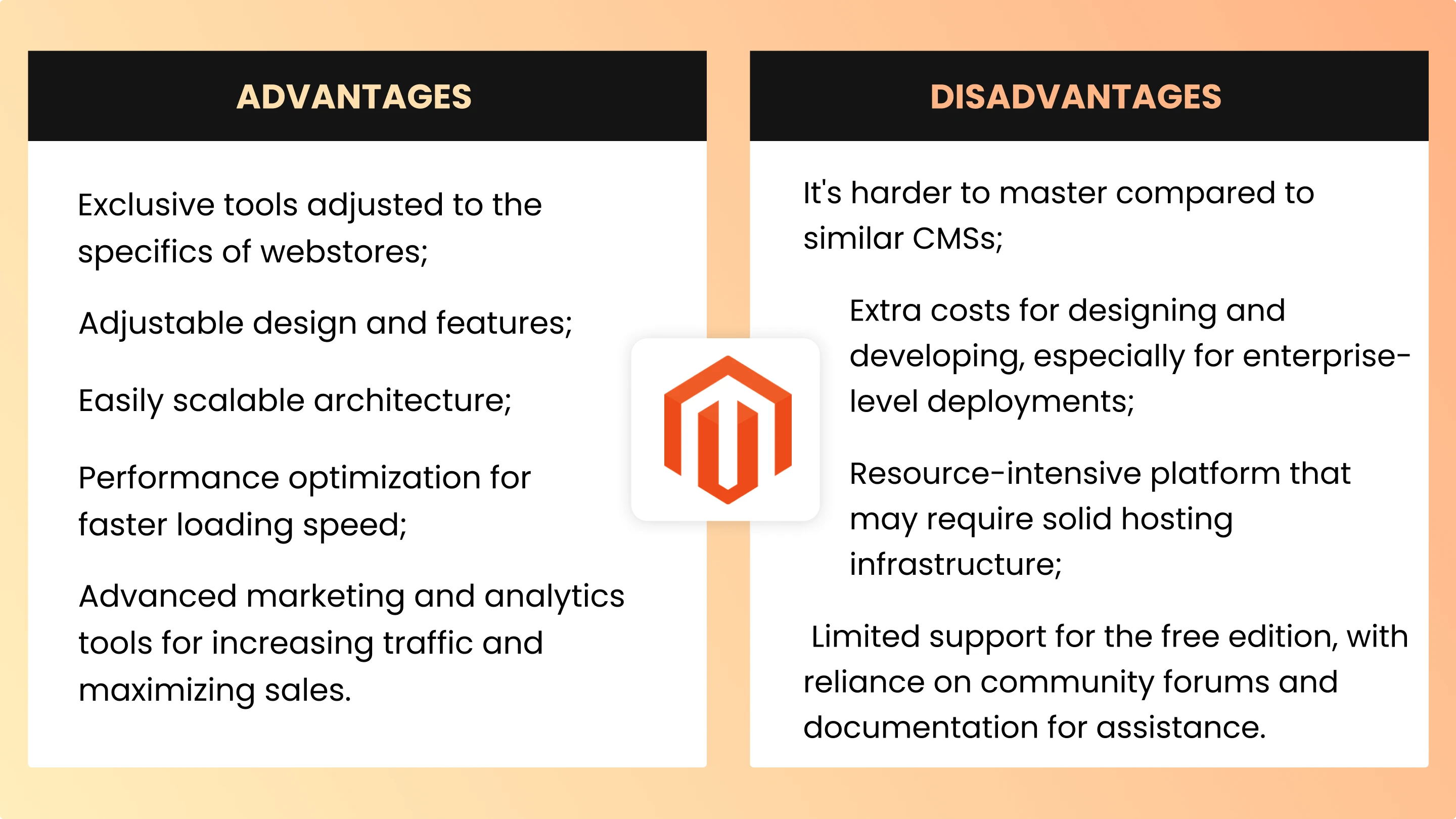
| Advantages of Magento | Disadvantages of Magento |
|---|---|
| Exclusive tools adjusted to the specifics of webstores; | It's harder to master compared to similar CMSs; |
| Adjustable design and features; | Extra costs for designing and developing, especially for enterprise-level deployments; |
| Easily scalable architecture; | Resource-intensive platform that may require solid hosting infrastructure; |
| Performance optimization for faster loading speed; | Limited support for the free edition, with reliance on community forums and documentation for assistance. |
| Advanced marketing and analytics tools for increasing traffic and maximizing sales. |
WordPress CMS
Main attributes
1. Simple Usage: The dashboard is highly intuitive, which facilitates newbies in launching their first e-commerce ventures and managing content with no prior tech expertise or development skills.
2. Third-party services: WordPress has a great number of themes and plugins, from design layouts to functional upgrades and integration with external services. WordPress is equipped with a toolset for creating diverse types of websites, including online shops.
3. Community Support: Within a lively community of developers, designers, and users of WordPress, you can participate in its continuous development, ask for assistance, and exchange valuable information and expertise.
4. SEO-Friendly Architecture: WordPress has a well-structured architecture, customizable permalinks, pre-installed SEO plugins, and responsive design features, all aimed at improving the visibility and rankings of websites on search engines.
WordPress Integration with WooCommerce:
WooCommerce, a widely used plugin for WordPress, turns it into a full-powered e-commerce CMS. After installing the extension, you can develop a product catalog, control stock, transactions, and shipping, all within the dashboard of WordPress. You can still enjoy the simple UX of WordPress and build dynamic and powerful e-commerce stores.
WordPress Users:
Small to Medium-Sized Companies. A seamless UX of WordPress and an enormous amount of plugins facilitate newbies to launch sophisticated webstores without employing technical experts or breaking the budget.
Content Creators. WordPress's roots as a blogging platform make it a great solution for content publishers, bloggers, and journalists.
E-commerce Entrepreneurs. With the assistance of WooCommerce and other external plugins, WordPress has become a solid CMS to sell goods and services online.
Pros and Cons of Using WordPress
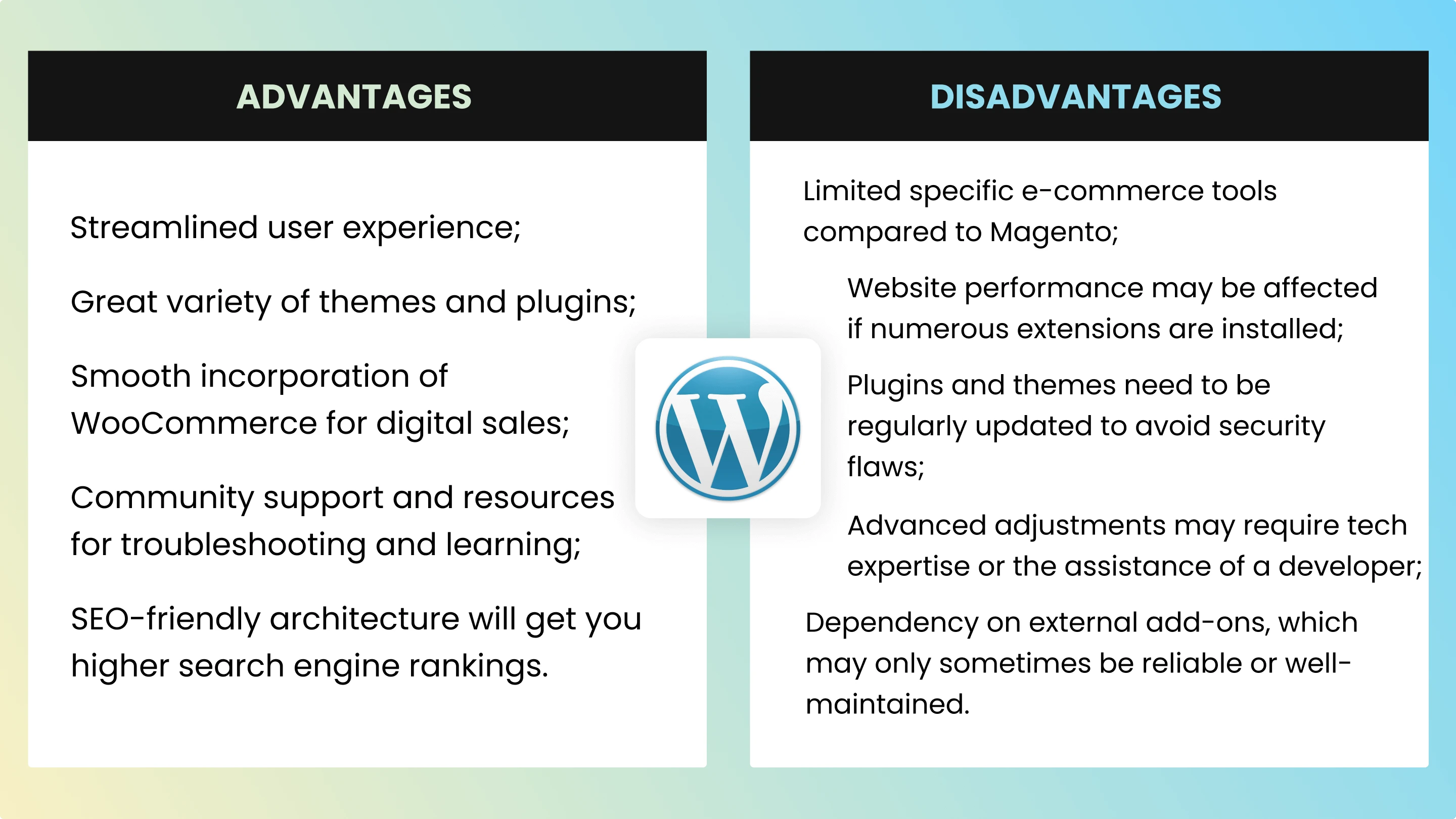
| Advantages of WordPress | Disadvantages of WordPress |
|---|---|
| Streamlined user experience; | Limited specific e-commerce tools compared to Magento; |
| Great variety of themes and plugins; | Website performance may be affected if numerous extensions are installed; |
| Smooth incorporation of WooCommerce for digital sales; | Plugins and themes need to be regularly updated to avoid security flaws; |
| Community support and resources for troubleshooting and learning; | Advanced adjustments may require tech expertise or the assistance of a developer; |
| SEO-friendly architecture will get you higher search engine rankings. | Dependency on external add-ons, which may only sometimes be reliable or well-maintained. |
How to Integrate WordPress into Magento?
Install Magento WordPress integration extensions. With add-ons, you can embed WordPress content directly to your Magento website, comprising blog content, webpages, and media.
Utilize WordPress as a content platform: Leverage WordPress's blogging features to develop engaging content, attract customers, and improve SEO rankings.
Improve your website content: Integrating WordPress into Magento makes content management processes straightforward so that you can operate both commercial and content-driven aspects of your store from one dashboard.
Grow SEO rankings: WordPress has native features that optimize content for search engines. You can engage more organic visitors and increase your position in search engine results.
Expand features with plugins: Employ various add-ons to optimize the website's features, add new extensions, and enhance the client experience.
Magento vs WordPress Ecommerce Differences and Comparison
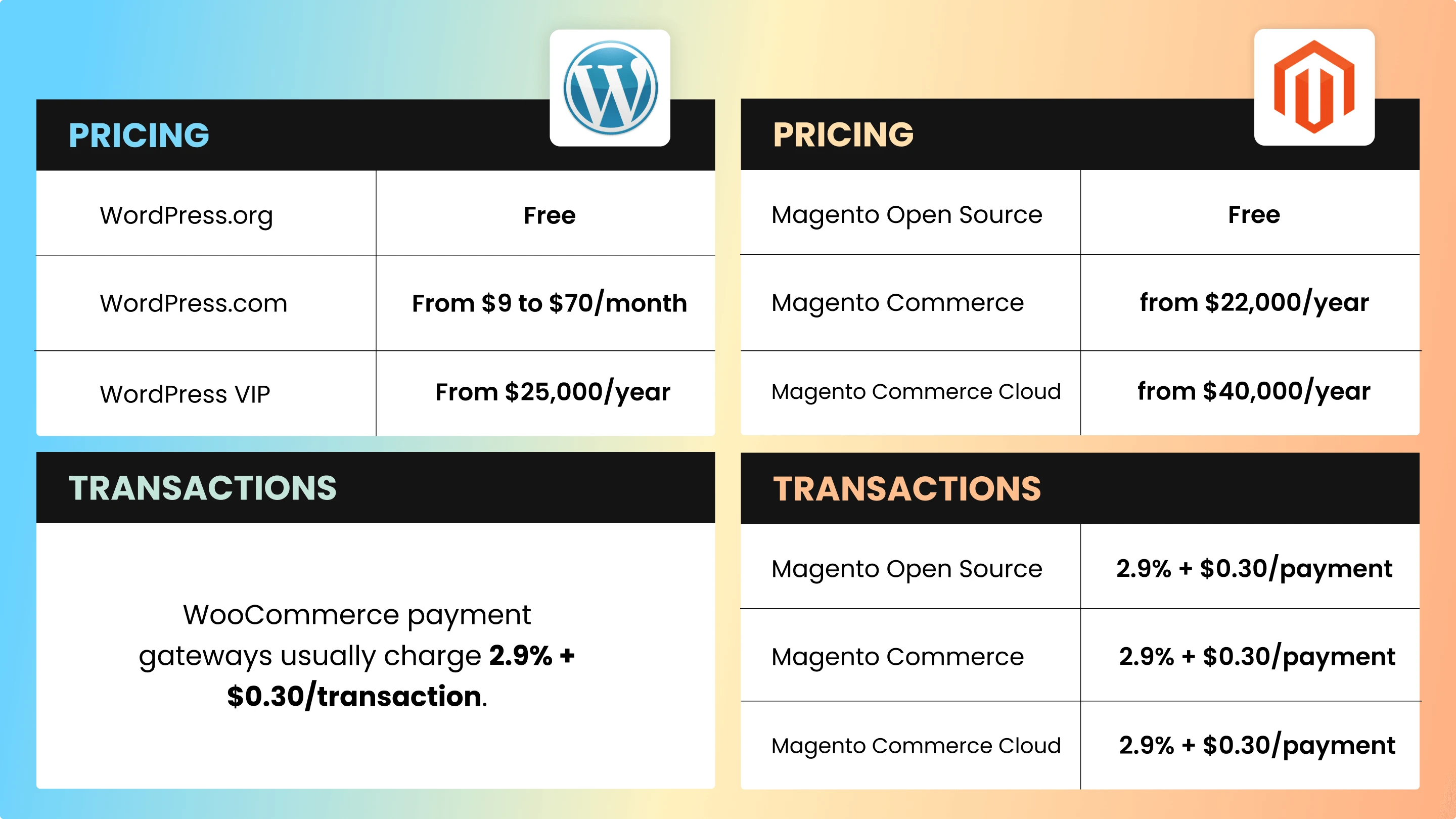
Pricing
Both Magento and WordPress offer free solutions. However, they do not include extra spending for hosting, domain, security, and scaling costs.
| Magento Pricing | WordPress Pricing |
|---|---|
| Magento Open Source: Free | WordPress.org: Free |
| Magento Commerce: from $22,000/year | WordPress.com: From $9 to $70/month |
| Magento Commerce Cloud: from $40,000/year | WordPress VIP: From $25,000/year |
Transactions
| Magento Transactions | WordPress Transactions |
|---|---|
| Magento Open Source: 2.9% + $0.30/payment | WooCommerce payment gateways usually charge 2.9% + $0.30/transaction. |
| Magento Commerce: 2.9% + $0.30/payment | |
| Magento Commerce Cloud: 2.9% + $0.30/payment |
Security Features
Magento Commerce has native security attributes like a Web Application Firewall and DDoS services, while Magento Open Source lacks these protections, requiring extensions for your data safety. Website administrators must control the add-ons’ performance and manually update them to address security issues. Failure to do so promptly can leave websites vulnerable to cyber attacks.
Similarly, the safety of stores built on WordPress relies on the proactive measures of its owners. Store owners have to update the installments on time and execute secure login practices. Despite remaining a prime target for cyber attacks, WordPress constantly reviews and updates its code. However, unlike Magento, WordPress has an auto-update function for plugins to keep security patches up-to-date.
Magento vs WordPress SEO Features
Magento utilizes some important SEO best practices, including responsive themes, optimizing meta descriptions and alt text, creating XML sitemaps, and increasing page indexing. However, these tasks often require manual execution. Therefore, Magento users familiar with SEO practices will be able to utilize its features to the maximum.
WordPress also has powerful SEO tools such as creating meta descriptions, headings, URLs, and responsive themes. Moreover, WordPress offers an enormous amount of SEO plugins and capabilities to optimize website code. Experienced users can streamline SEO performance and indexing by removing redundant code, while non-tech-savvy users can only rely on plugins for automation. WordPress hosts a broader selection of SEO tools, becoming accessible to store owners with different expertise levels, simplifying the SEO automation process for online stores.
Usability
The full set of Magento features is hard to master without tech proficiency and coding expertise to use all its opportunities. Conversely, WordPress is accessible to users across various skill sets, including beginners, owing to its streamlined UX.
WordPress compared to Magento is remarkable for its simplicity. It is becoming a superior alternative for small shops lacking extra funds for employing external developers. Its ease of use empowers users to use the platform with confidence, facilitating efficient store operations and content creation.
What To Choose: Magento or WordPress
Deciding between Magento and WordPress comes down to grasping their fundamental distinctions.
Magento delivers a set of specific features designed for online trade and smooth scalability solutions. It is a great platform for growing enterprises with special industrial requirements. However, you will likely need to employ in-house or external developers to launch and maintain your store.
WordPress is more accessible to users with basic or no tech expertise, suiting small shops and humble budget capabilities. With a great choice of external add-ons and an easy-to-use dashboard, WordPress is an alternative for companies to build and operate their store quickly.
Wrapping Up
If you're unsure whether to pick Magento or WordPress, consider these suggestions:
Evaluate your unique business demands. Estimate your operations requirements, growth plan, and development expertise within your team.
Consider long-term scaling. Evaluate your company's growth trajectory and requirements. Magento might be a better choice for fast-growing enterprises with specific needs, while WordPress offers flexibility for smaller online shops to scale gradually.
Evaluate tech expertise. Consider the software development proficiency available within your internal resources. Installing Magento requires a certain level of tech-savvyness, whereas WordPress offers a more accessible process suitable for newbies.
Review budget constraints. Assess your financial limitations, including initial installation costs and ongoing operation budget. Magento may require a higher upfront investment, particularly for enterprise-level deployments, whereas WordPress has more affordable offers for small businesses.
Explore flexibility opportunities. Examine the scale of adjustments and personalization you may want to apply for your online store design and user experience. Magento provides higher flexibility, while the themes and plugins provided by WordPress are less inclined to e-commerce needs.
Examine security and support features. Magento and WordPress offer built-in security features and free community resources, however, Magento may require more manual updates and maintenance.
Check user feedback and reviews. Evaluate what businesses similar to yours say about their experience with Magento or WordPress. This can open alternative perspectives on each platform's practical experiences and challenges.
Ultimately, evaluate and keep in mind unique business strategies, tech capabilities, financial limitations, and growth objectives. By carefully assessing these factors and aligning them with the plans offered by each platform, it will be easier for you to make a data-driven decision that sets the solid ground for a successful future of your e-commerce venture.




