Magento Security Check: Protect Your Store from Vulnerabilities
-
 Eugen Barilyuk
Eugen Barilyuk
- Magento 2
- 13 min read
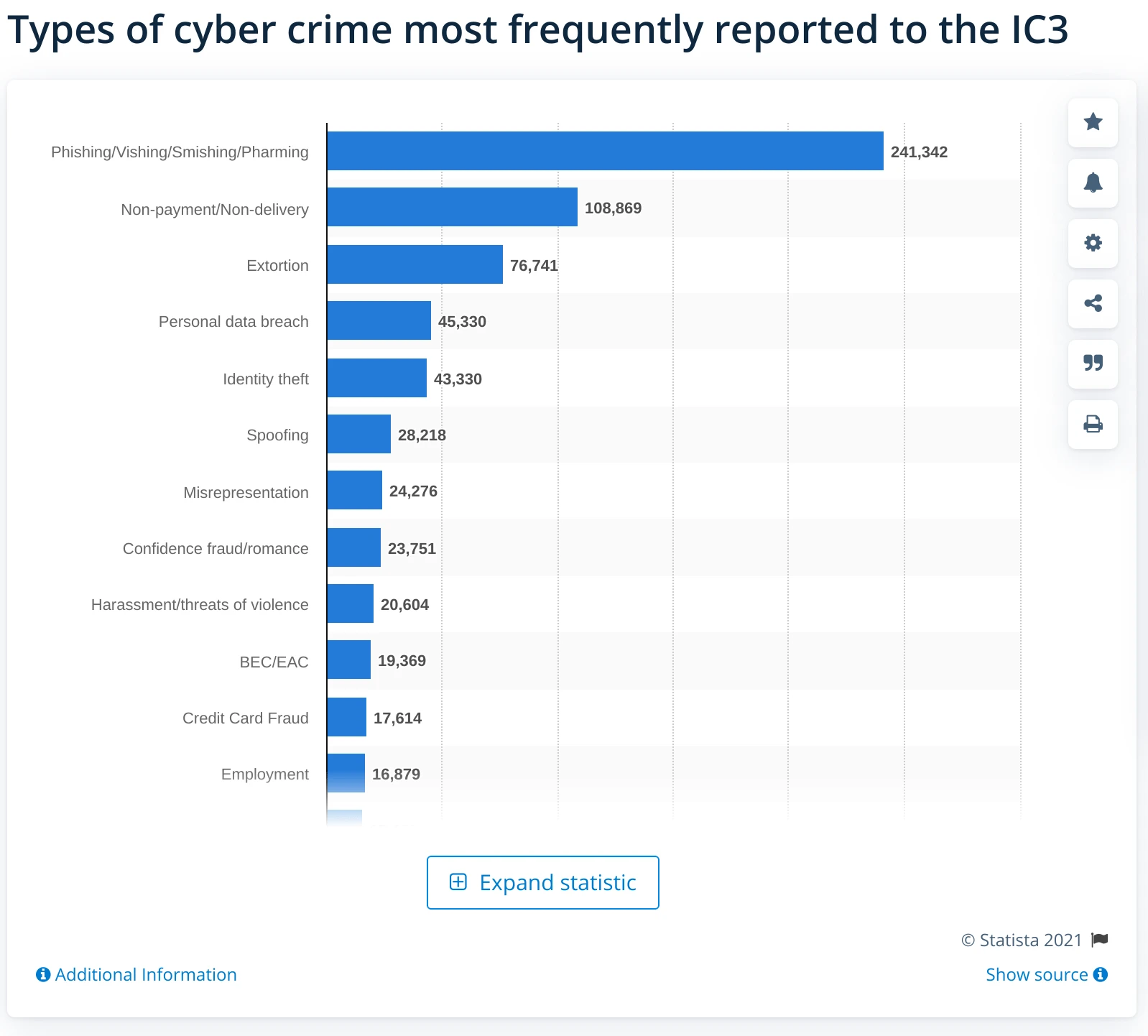
While you think your store is working perfectly fine it may secretly earn money for cybercriminals. In the age of digital transformation, cybersecurity is becoming a constant and growing concern for businesses, since cyberattacks and malware pose a close threat - almost one in three eCommerce businesses have suffered financial losses due to cyberattacks.
By 2024 global losses will amount to $5.2 trillion, and one cyber attack costs businesses an average of $200,000.
Small businesses are one of the primary targets for cybercriminals accounting for about 43% of attacks. The cost of cyberattacks for SMB has grown in 2018 and 2019, from $3,000 to $9,000, respectively.
The financial and reputational losses the small businesses may suffer after the attack can be devastating. About 60% of SMBs shut down within 6 months of a major cyberattack.
As both monetary security and the fate of your business are on the line, it's pivotal for a Magento store to check for suspicious code and see known weak points. Cybercriminals are constantly seeking for new vulnerabilities, so the store owner should increase their efforts in the task of protecting their store.
Since one in four (25%) senior decision-makers at SMBs say they don’t even know where to start with cybersecurity efforts, this article elaborates in detail on how to get started.
Top security threats for eCommerce
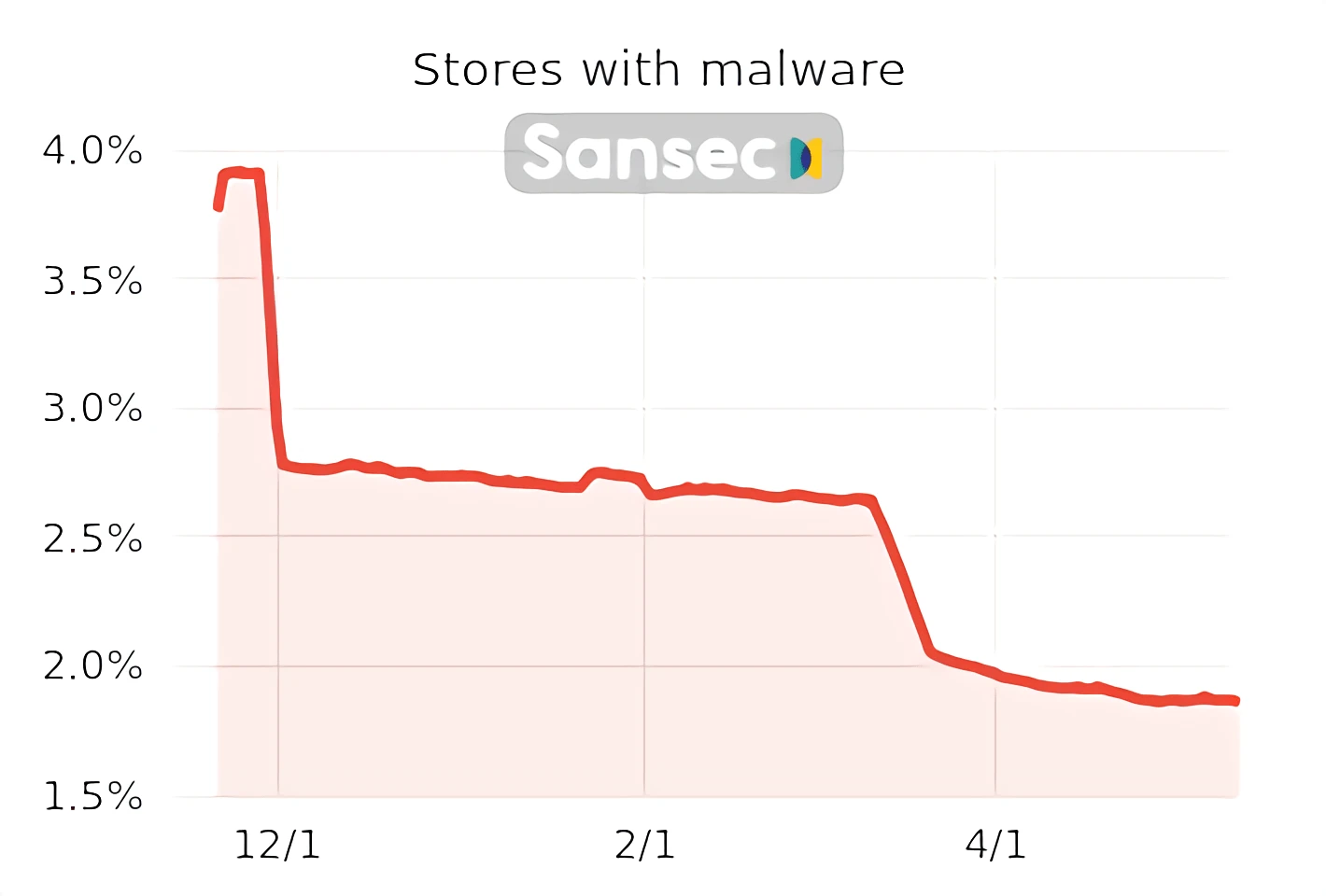
Magento is a very secure eCommerce platform, and the number of Magento stores with malware has dropped from less than 4% to less than 2% for the last six months, according to Sansec:
The major reason for this high security level is the constant work of Adobe software engineers, who relentlessly release patches for known vulnerabilities.
The latest Magento 2.4.2, as of this writing, has received over 35 security enhancements. These patches close several significant vulnerabilities, including remote code execution and cross-site scripting (XSS).
However, cybercriminals seek new vulnerabilities, leaving about 87% of stores on the Magento platform at high risk of cyberattacks. Here are the top security issues retailers should watch out for:
E-skimming
E-skimming, which is also called web skimming or Magecart, is credit card fraud that is conducted by exploiting a security breach in a store's software code.
Attackers use the vulnerability to install malicious software and steal customer credentials when they enter their payment and personal information on the payment processing page.
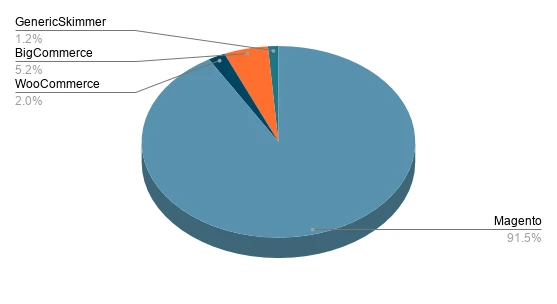
Historically, the Magento platform has been the most highly targeted in skimmer attacks:
This type of fraud was first reported in April 2015 and has grown so large that the FBI issued a public warning to online retailers.
A year later there was a record-breaking Magecart hack on Magento stores, which resulted in 3% of the total Magento 1 installation base (2806 stores) being breached. Magento 1 is still operated by more than 70 000 stores worldwide, according to Sansec.
Magento 1 has reached its End-Of-Life at the time of this record-breaking attack, and the bad actor, selling the Cardbleed exploit, stressed that no official patches would be provided by Adobe to close the zero-day vulnerability, used by the exploit.
Ransomware
Ransomware is malicious software intended to obstruct admittance to a computer system until an amount of cash is paid. Typically, the normal access to the computer or server is obstructed by encrypting the data on its drives. The owner loses his documents, data sets, applications.
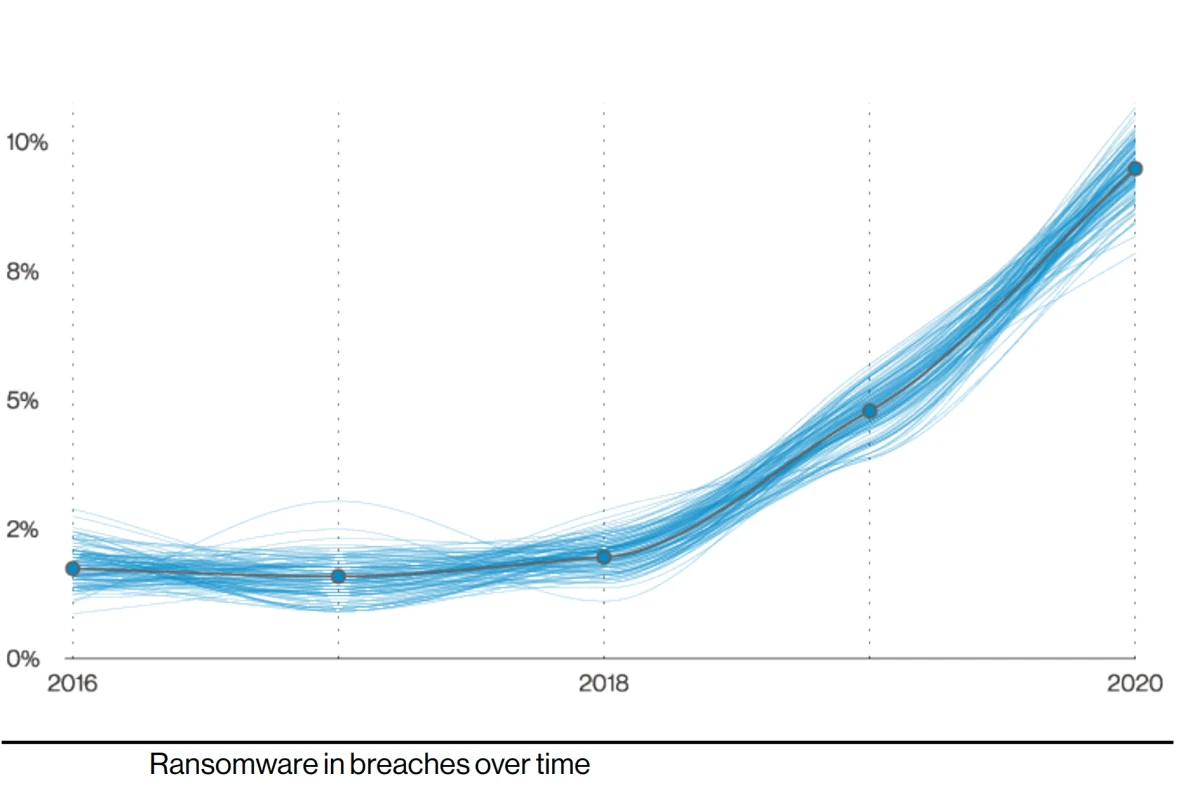
Ransomware attacks become more frequent every year: Cybersecurity Ventures estimates that in 2021 a ransomware attack occurred every 11 seconds, up considerably from every 40 seconds in 2016.
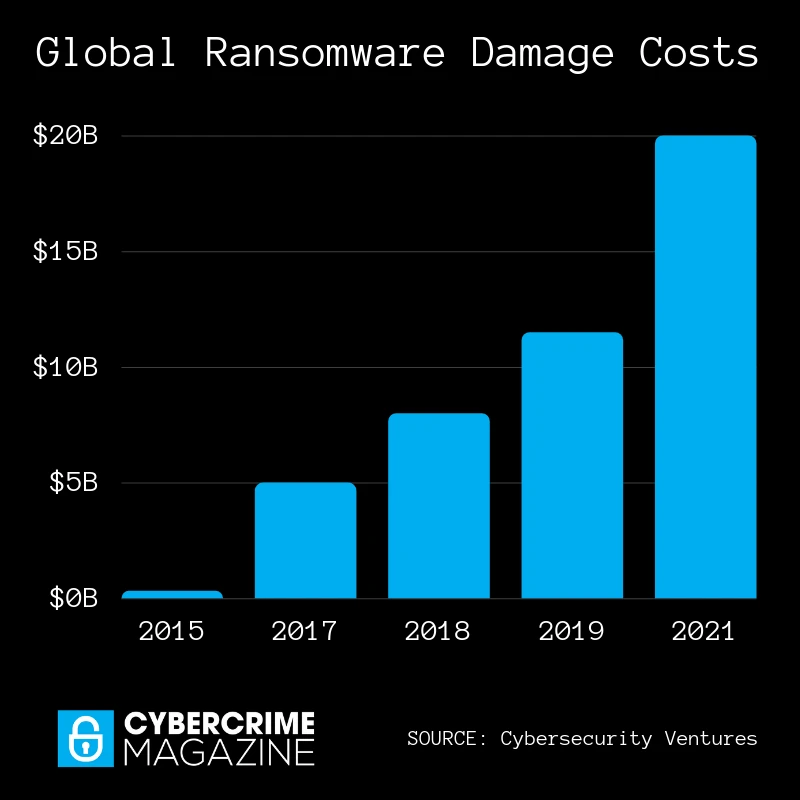
At the same time, such attacks bring more damage to businesses. The average ransom payment increased from $5,000 in 2018 to $200,000 in 2020. The total damage from ransomware attacks is estimated to reach $20bn – 57 times more than in 2015.
This tremendous ascent in ransomware assaults is generally due to the business owners who are willing to pay. About 70% of ransomware victims paid after being hit with ransomware, according to IBM X-Force.
The most widely recognized strategies bad actors use for ransomware assaults are email phishing, the use of RDP and software vulnerabilities.
DDoS
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack floods your website’s servers with requests from thousands of devices, which nowadays are often breached IoT devices. Such attacks cause an entire site to go offline.
This leads to direct financial losses as customers are unable to buy at a DDoSed store. The average cost of a DDoS attack is $218k. This type of attack also leaves the website open to a malware infection.
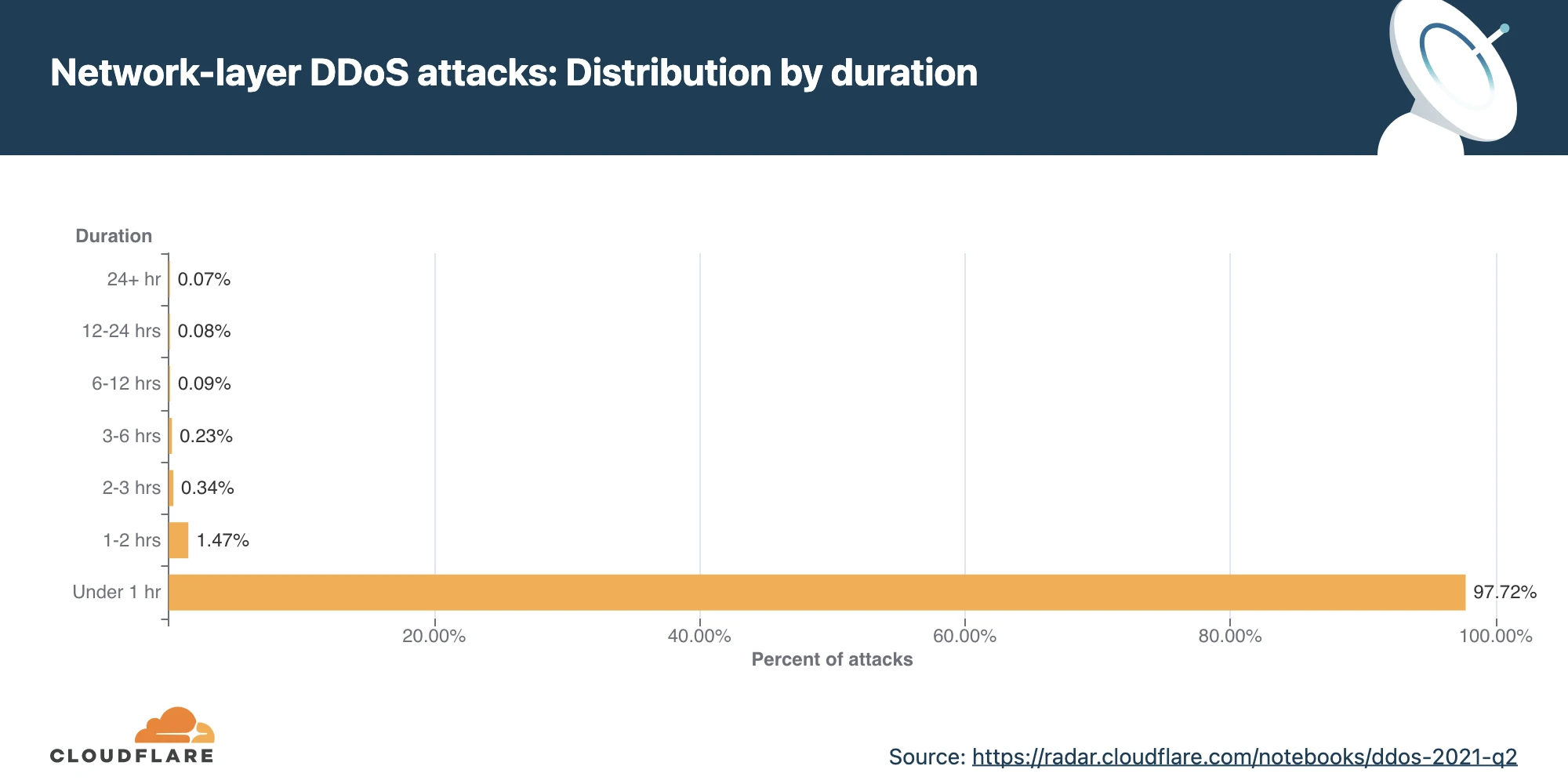
The frequency of DDoS threats to e-business is on the rise, particularly during peak sales periods. The number of DDoS attacks increased 41.8% in 2021 H1 compared to 2020 H2. Over 11% of DDoSed victims report receiving a ransom demand letter prior to the attack.
Phishing
Phishing is one of the oldest malicious techniques, but it is still among the most popular security dangers. It uses the human factor to get sensitive data like logins and passwords or infect organizations with ransomware and other types of malware.
Cyber aggressors are anxious to take advantage of any web based business that hasn't put resources into appropriate preparing its staff on phishing mindfulness and other network safety dangers.
When a cybercriminal obtains access to the store system using login credentials with executive rights, there's a great deal of damage that your business could endure.
Brute-force
Brute-force is a rather straightforward method of hacking - access to accounts is obtained by guessing passwords. It is relatively effective: 80% of breaches are perpetrated from weak and stolen passwords, according to World Economic Forum.
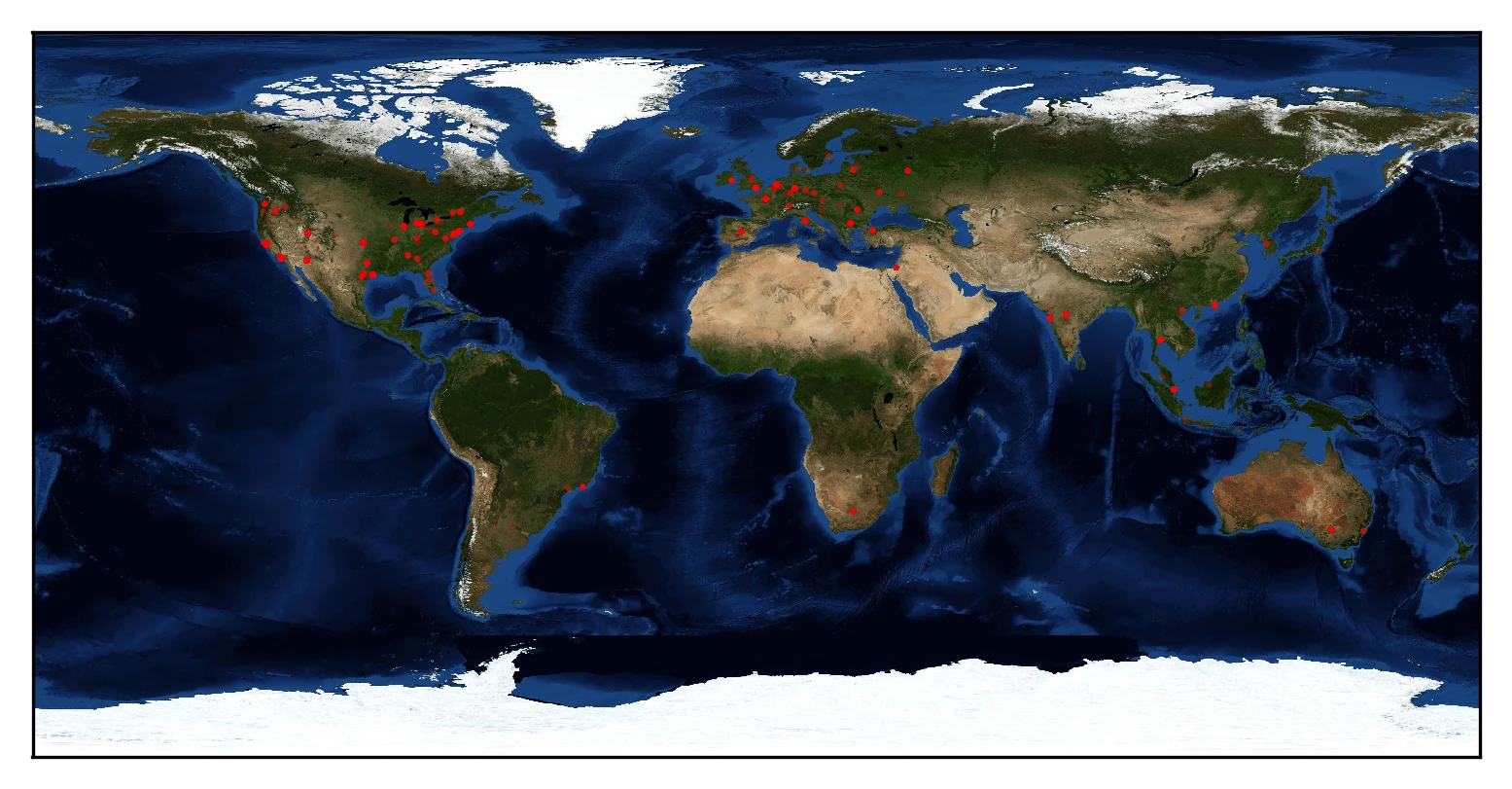
Magento stores are no exception to the brute-force method. Flashpoint found on deep & dark web forums credentials of at least 1,000 Magento admin panels. These Magento sites were located all over the world:
Best security practices for Magento store
While there is no single way of taking out all security dangers, there are several things you can do to transform your store into a less alluring objective for cybercriminals. Read on Adobe Magento Commerce Security Best Practices Guide. Additionally, stick to the following practices:
Magento Admin panel security enhancement
Do not access your Magento Admin from any available computer. Make sure that only trusted secure computers are used to work with the Magento Admin panel. On this computer utilize a malware scanner or antivirus, install patches regularly, avoid questionable software and network connections.
Limit admittance to the Magento Admin by using a whitelist with the IP addresses of every PC that is approved to access the Admin panel. Additionally, change the default admin panel URL.
Utilize two-factor verification to access the Admin panel. In this case, an extra password is used which is created on your telephone through a Google Auth app, or a special authorization gadget. Starting from Magento 2.3 this functionality is built-in:

Login into the Magento Admin panel with a password that cannot be brute-forced. Change it intermittently to protect your Magento from possible leaks or theft credentials that you may not be aware of.
For example, in 2020 a hosting provider allowed 63 million credentials to be leaked, including Magento login details. Do not store FTP passwords in FTP programs, as they are a target for malware.
Set read-only file permissions for Core Magento and directory files.
Utilize CAPTCHA for further security when admin and customer login.
Avoid phishing by training your staff not to click on suspicious links, skip suspicious emails and apps. The report shows that 1 in 3,000 emails contains malware, and the average employee receives 121 emails per day. An organization with 100 employees will receive 4 infected emails every day.
Conducting at least 11 instructional classes for your staff over 4-6 months reduces the percentage of phishing message clicks by 65%.
Monitor attack signs
Newly discovered vulnerabilities and delays in patching already known ones, leave a chance for cyber attackers to breach your store. It's a good practice to conduct periodic security reviews looking for signs of a breach. Here is what to look out for:
Unauthorized admin logins and new users with admin rights. Adobe Commerce edition provides Actions Log tracking of suspicious activity.
Monitor system logins (FTP, SSH) for suspicious activity, uploads, commands.
Magento stores on an Apache web server can use an automated log analyzer Apache Scalp, which aims to look for security problems.
Review the logs available from your server hosting provider. Implement an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) on your network.
Monitor the Magento file integrity extensions to receive notifications of possible malware intrusion.
Prepare for cyberattack with a plan
Almost 60% of decision-makers at SMBs say they do not have a cyberattack prevention plan. However, having such a plan in place can significantly mitigate the consequences of a cyber disaster. About 96% of companies with a trusted disaster recovery plan were able to survive ransomware attacks.
In case you don't know where to start with your cyber disaster recovery plan, you may want to use a Guide for Cybersecurity Event Recovery by the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Basic steps in case of cyberattack
In the event of an ongoing breach, you may want to contact with IT security team, the hosting provider's support to determine the scope of the attack and receive suggestions to mitigate the consequences for your business.
At the same time you can do the following actions in your store:
Block access to the store, to preserve possible evidence of intrusion and minimize data stealing;
Make a backup of the breached server to have evidence of installed malware or compromised files;
Try to figure out how and when the store was compromised by reviewing logs and file changes;
Wipe everything and reinstall the system from a clean backup;
Apply all security patches to prevent the attack from repeating;
Reset all-access credentials;
Inform your customers in compliance with the law requirements.
How to check Magento store for malware and vulnerabilities
A Magento store owner can start evaluating the cybersecurity of his business with Adobe Security Scan. This is a free tool available both for Adobe Commerce and Magento Open Source editions.
This malware scanner is maintained by Adobe in partnership with Sansec, a leading eCommerce malware detection company. Through this partnership, the scanner obtains about 9,000 malware signatures.
The Adobe Security Scan offers Magento website scanning for:
- Potential malware and vulnerabilities on the web store
- Out-of-date security patches
- Potentially vulnerable extensions
- Digital skimming injections
- Security misconfigurations
Security Scan runs a total of 21,000 tests to check Magento stores for potential malware. It offers scheduled security scan and provides access to historical reports for tracking the security progress of your store.
Prerequisites
In order to use the Security Scan tool, a Magento store owner must first obtain a Commerce Marketplace account. To register this account, navigate to account.magento.com.
On the main account page navigate to the Security Scan tab and familiarize yourself with the tool by reading Magento Security Scan Tool Overview, Security Scan Tool FAQ, Security Scan Tool Onboarding documents provided in PDF.
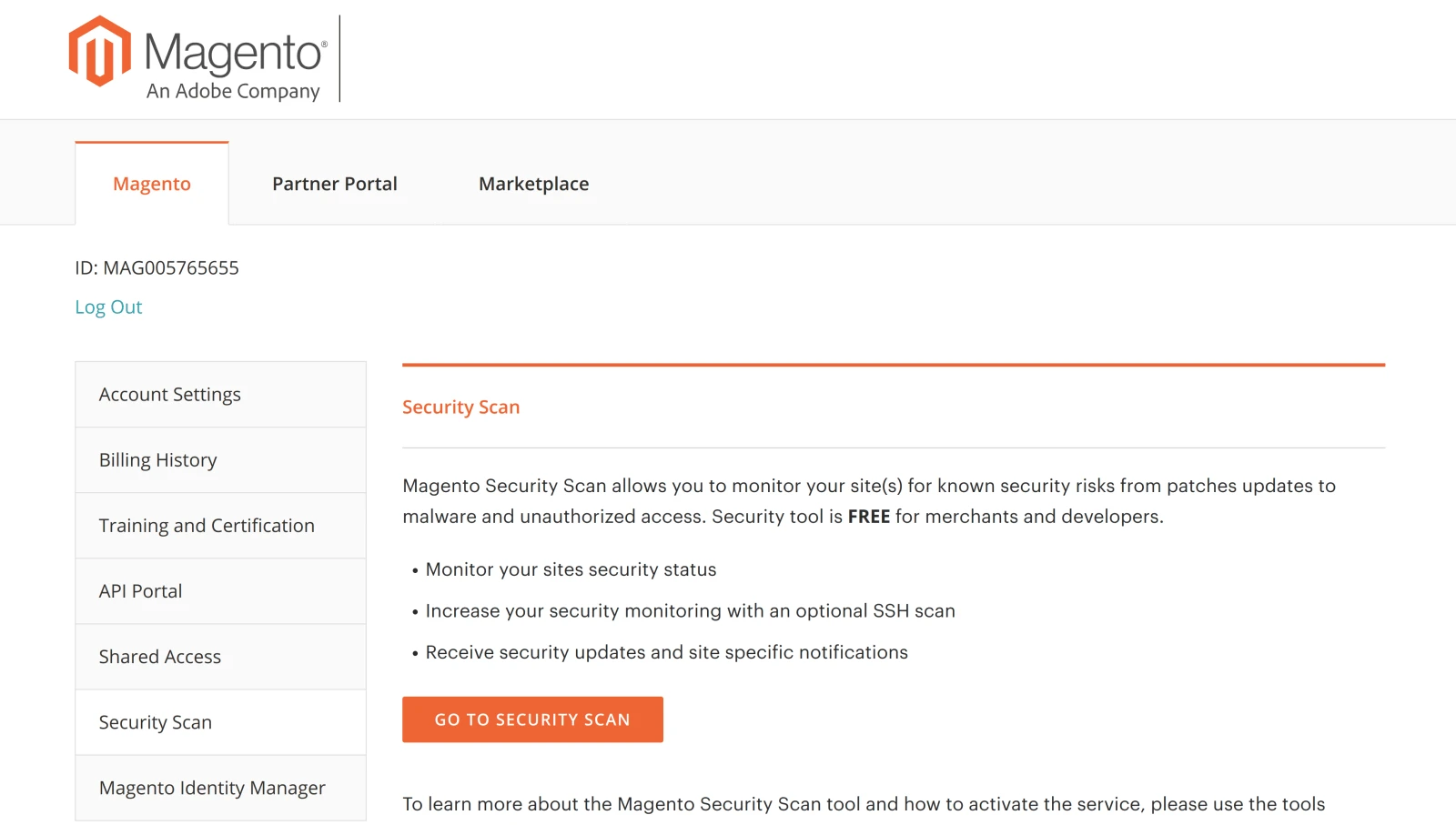
Click Go to security scan and accept the terms of Magento Web Scan Service Addendum to grant access to the Magento scanner.
Scanning Magento for security dangers
To launch the Magento scanning process you first need to add your store's website to the scanner by clicking Add site button.
Security Scan can only be used by the store owners and authorized persons. This condition is met through the ownership verification process. The store owner must add a special tag to the source code of his Magento store.
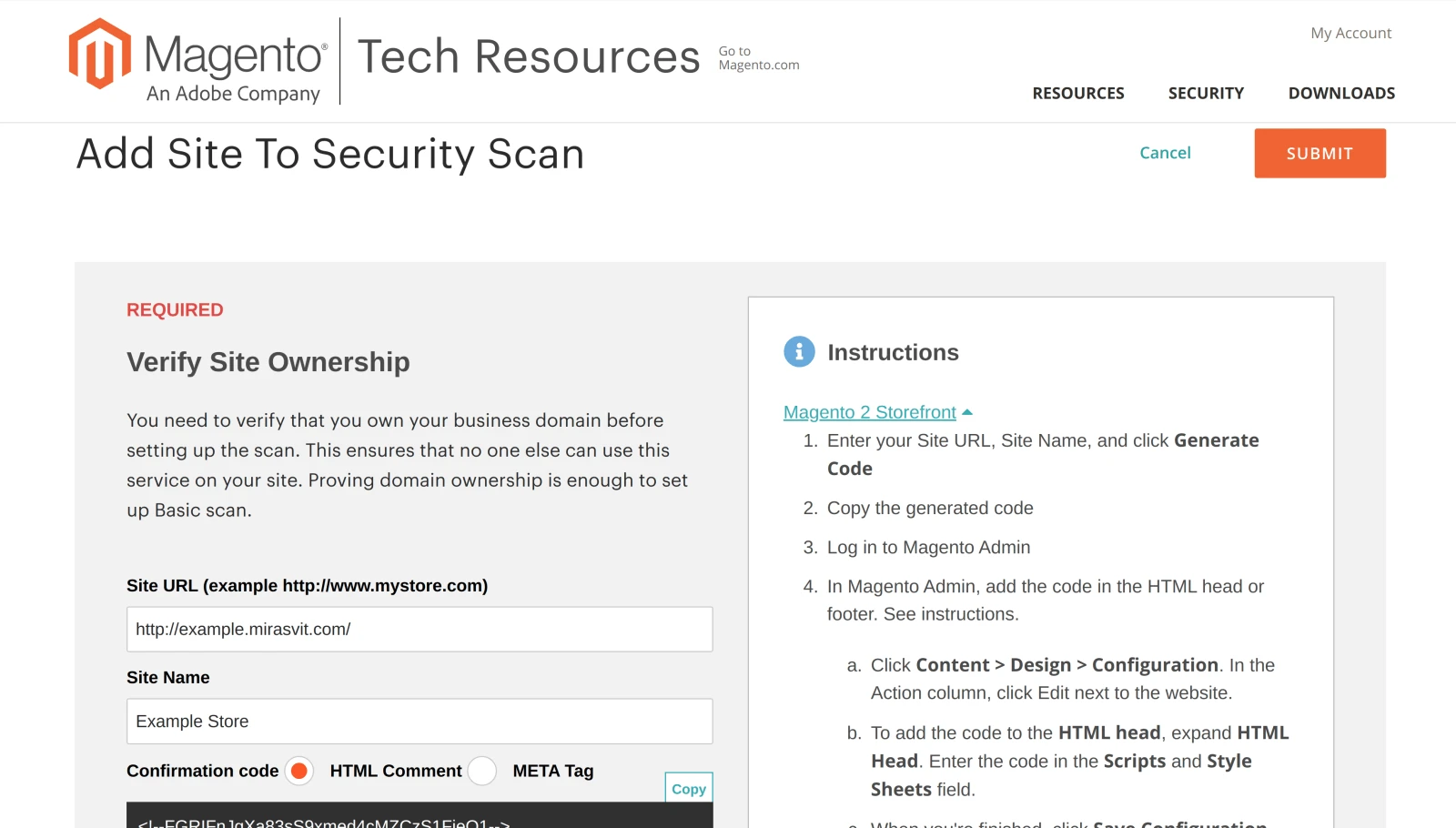
Verify Magento store ownership
Store ownership verification can be done by adding an HTML Comment or META Tag on each page of the Magento store.
To add this verification marker in the admin panel of your store, navigate to Content > Design > Configuration. Choose the Website and Store View you need to verify and click Edit.
Scroll down to the HTML Head section where the field Scripts and Style Sheets is located. Insert here the HTML Comment or META Tag provided by the verification page of the Security Scan.
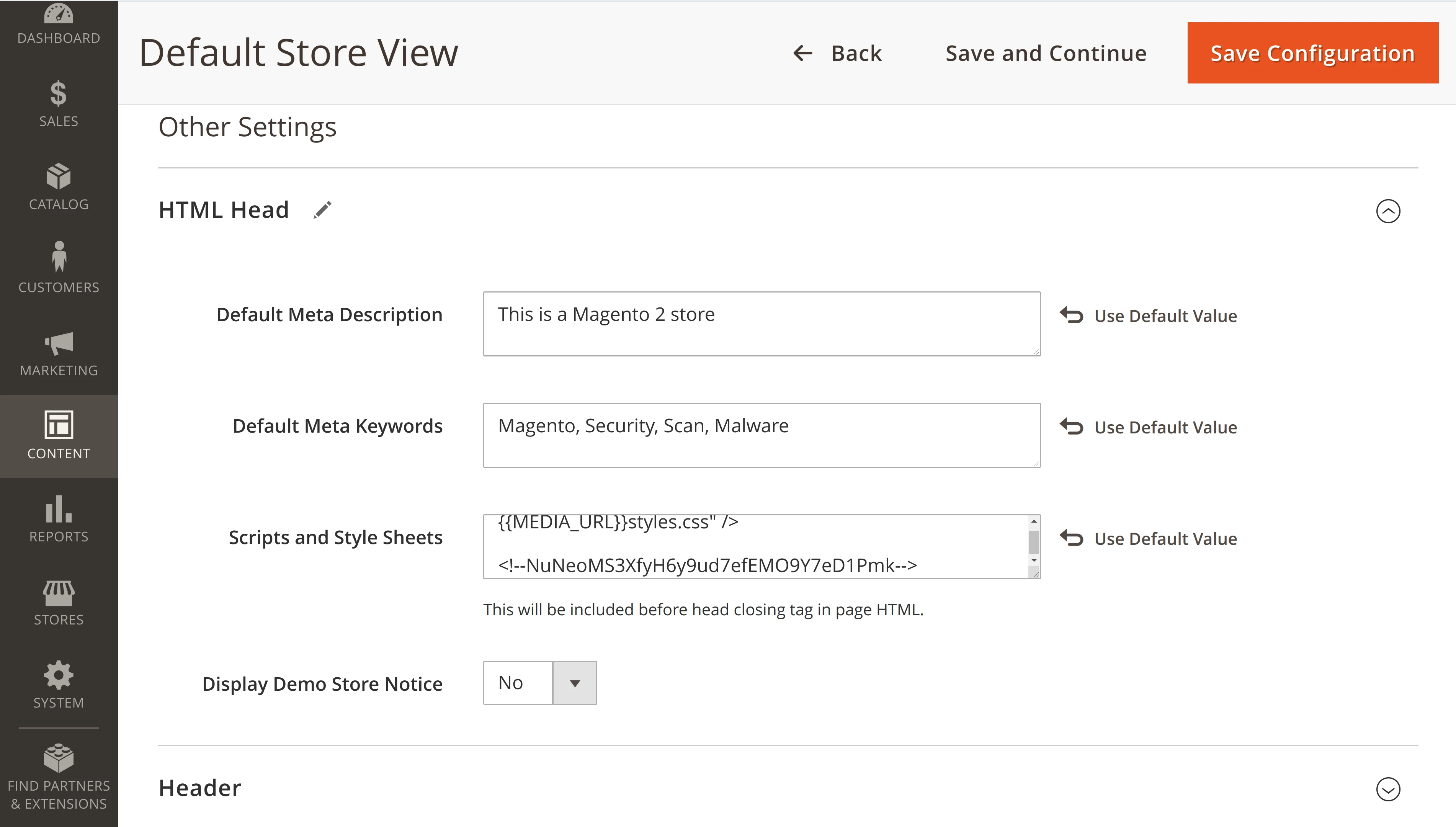
Save the new configuration, and clear the cache in your Magento store. In a web browser, open the source code of any page in your store and make sure the verification code is present in the section.
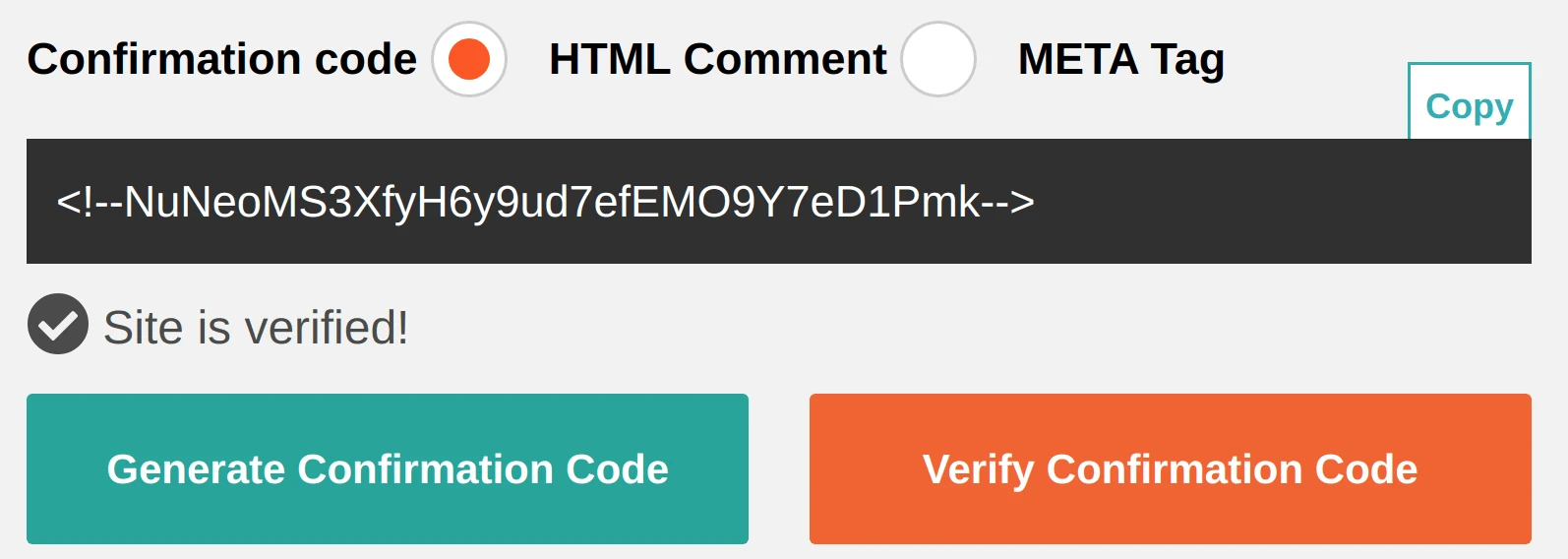
Go back to the Security Scan verification page and click Verify Confirmation Code. In case of successful verification a corresponding mark will be displayed:
Configuring Magento scan options
Below the verification section, the Security Scan tool offers several configuration options:
Set up SSH Scan. Offers database scan, and file integrity check. Currently under development and is not available.
Set up Automatic Security Scan. Configure the scanning schedule with three options: weekly (recommended by the tool), daily, do not automatically scan.
Report notifications. Allows getting security updates via emails.
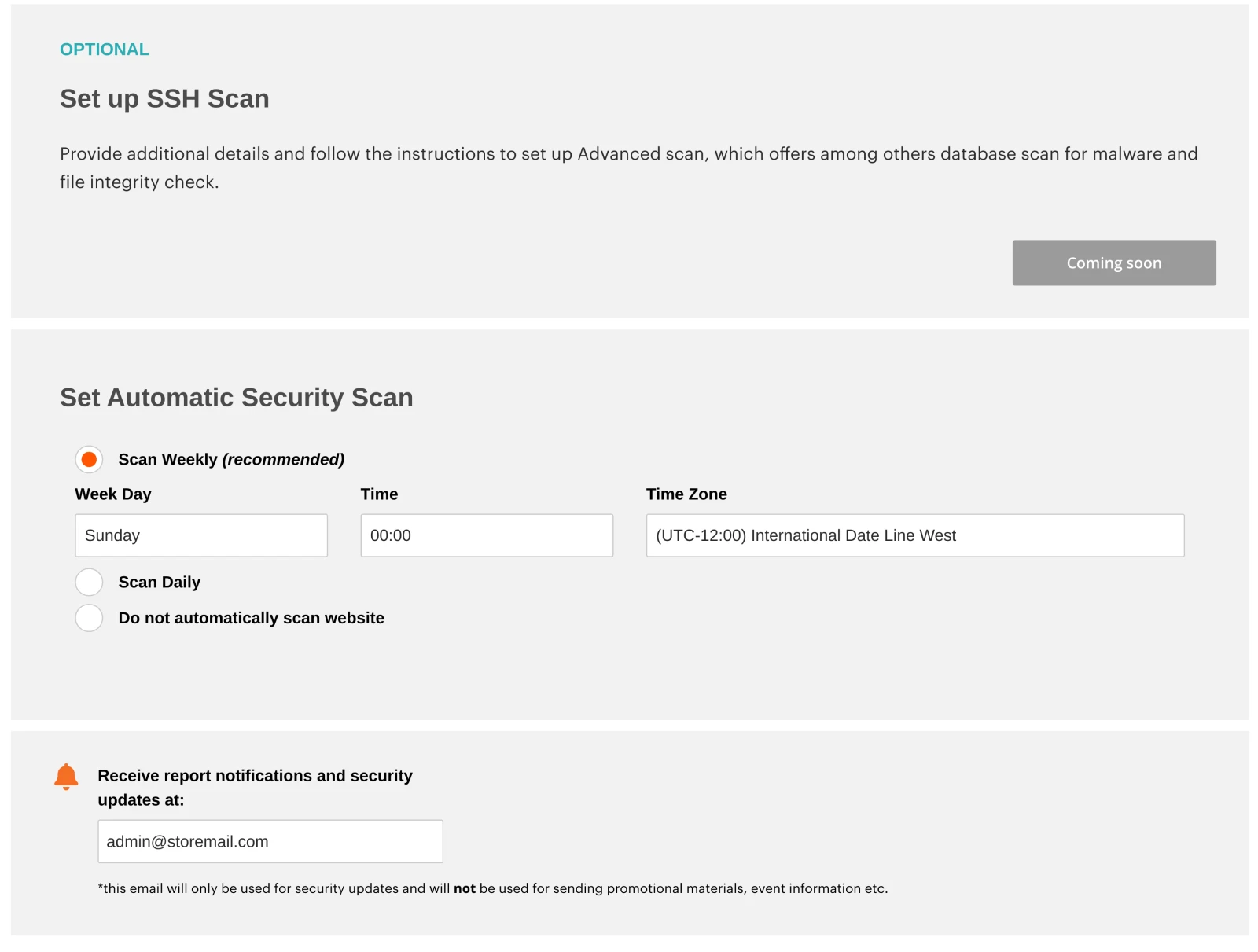
After finishing site ownership verification and scan tool configuration, press Submit
Launch security scan
Return to the previous page of Monitored Websites where you should see your store listed. Click on the Action menu and select Run scan to launch the scanning process immediately. Alternatively, wait until the scanner will be launched by schedule.
Magento Security Scan report
Once your store scan is complete, you can check the report. Additionally, Security Scan summarises its findings in the Risk column for each added website.
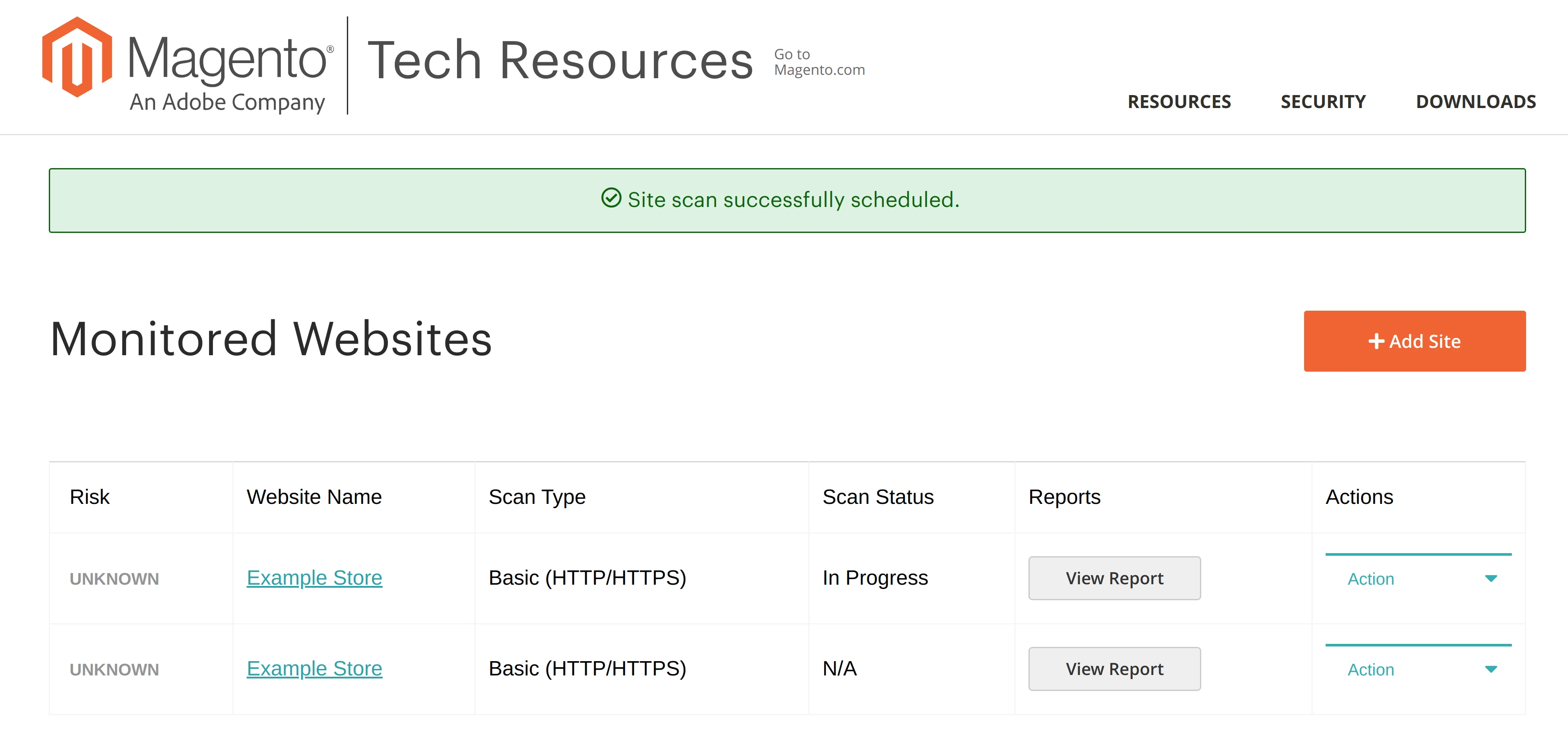
For new sites that have never been scanned before the Risk status will be set to Unknown, and the scan status will be N/A. If the Magento store is currently being scanned, the scan status will be In Progress.
The scan report is available as a web page, as well as a PDF document for download.
The Security Report contains information on such security problems:
- Failed Scans. Shows vulnerabilities present in your store and gives a brief description of them.

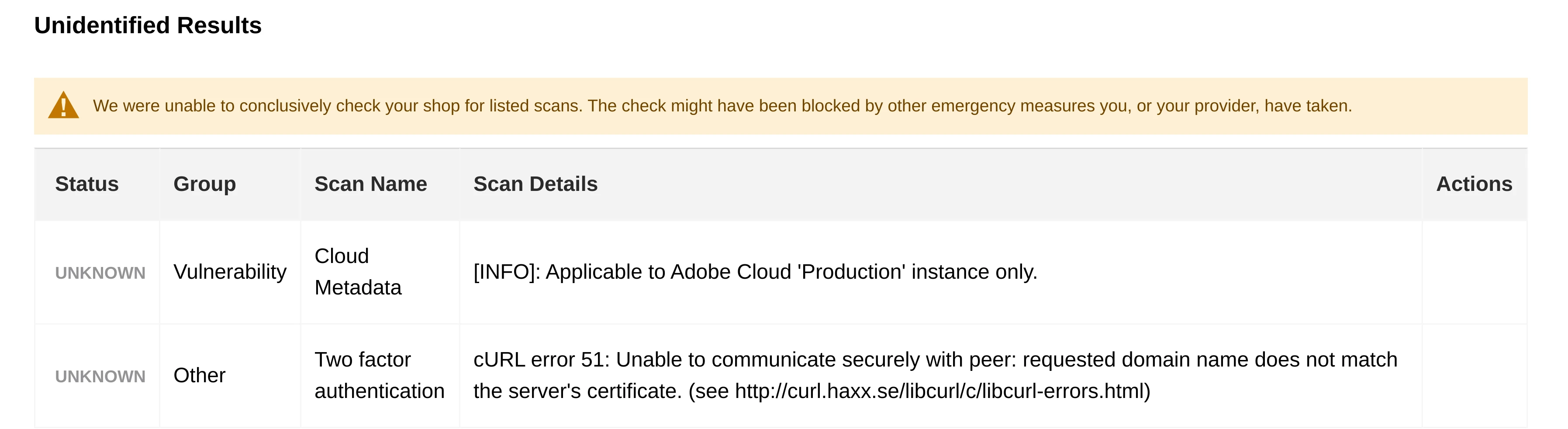
- Unidentified Results. Displays possible weak points in the store that the Security Scan tool could not reliably detect due to some restrictions or blockages in your store.
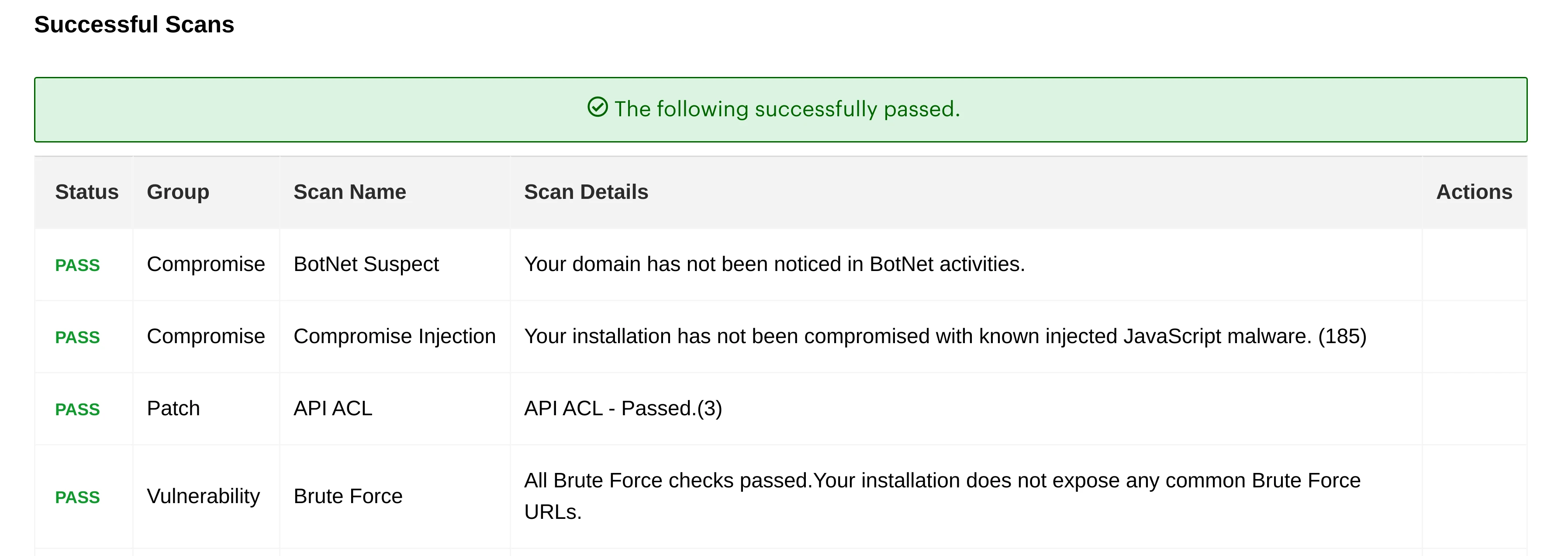
- Successful Scans. Shows a list of known vulnerabilities that your store is protected from.
For some active vulnerabilities, the Security Scan tool can provide information on how to resolve them. If this information is not available, you may need to enlist the help of IT security experts.
Summary
Ecommerce entrepreneurs regularly expect software designers to address security issues in a way they don't have to worry about. The truth is that developing agencies have great expertise in creating excellent, value-based sites that sell products. However, their aptitude on security issues is, for the most part, not deeply profound.
Magento store owners should be aware of eCommerce security issues, as even a solitary cybercriminal intrusion can be a total destruction for a small eCommerce business.
Basic safety measures can have a genuine effect on diminishing the level of danger for the online business. Installing security patches, changing default settings, utilizing stronger passwords along with multi-factor authorization are helpful in the task of defending from cybercrooks.
However, the hazard can never be completely eliminated, so organizations should to likewise consider putting resources into cybersecurity. Leveraging the services of online security experts and developing a digital protection strategy can bring the most benefits.
Until then, you can administer basic cybersecurity strategies and start protecting your store with simple and free tools, like Adobe Secure Scan.