Adobe Summit 2022: Key Insights and Takeaways for eCommerce
-
 Eugen Barilyuk
Eugen Barilyuk
- Mirasvit Blog
- 15 min read
Adobe Summit is the largest event in the Magento world that discloses the most prominent eCommerce technologies and trends over several days. The future brings several major problems for eCommerce to cope with, and stores along with industry experts have ideas on how to increase revenue in such an environment. We've attended this conference to tell you what can be expected in online commerce in months.
- Three predictions on the digital economy
- Self-driving stores
- Top CMS Innovations
- B2B marketing automation in 2022
- How to use Log Forwarding to monitor your Compute Worker
- Summary
Three predictions on digital economy
Adobe published three main predictions in the eCommerce sector for the near future, right before the beginning of the Summit. The data is based on the Adobe Digital Economy Index, which is the most comprehensive barometer in the industry, analyzing over one trillion transactions to provide a real-time pulse on major trends.
This year Adobe projects that eCommerce in the U. S. alone will drive one trillion dollars in spending for the first time. The main growth will be in digital grocery shopping. Groceries drove $72 billion in online spending for 2021, which is bolstered by lasting habits from the COVID-19 pandemic.
Adobe expects the groceries will be a top category and eCommerce for the long haul, one day exceeding one hundred billion dollars a year.
The second prediction relates to the longstanding trend of prices reversing. Almost $22 billion of inflation was driven by higher prices.
While online shopping is typically considered cheaper than buying offline, this will change in the future.
The third prediction regards the supply chains - problems with suppliers will continue to impact the digital economy. As a result, consumers will see billions of out-of-stock messages in the months ahead. According to Adobe, they have seen 12 billion out-of-stock messages for the last four months.
Self-driving stores
The online store requires lots of manual work to show the best operational results and stay in touch with its customers. So, what would you say if your store would do its daily routine automatically? Meet the concept of self-driving stores. Ryan Rozich – a product director at Adobe – explains it in detail.

Almost 86% of customers say personalization plays a role in their purchase, and most shoppers say they chose recommended or paid more for brands to deliver these personalized experiences.
Merchants have lots of options to deliver the experience shoppers expect; however, it requires an intimate knowledge of product relationships and merchandising rules. From page content to search configuration, emails – merchants spend a lot of time making thousands of little decisions.
Personalized shopping experience brings results - Amazon reports that over 35% of their overall sales are directly attributed to personalized recommendations.

This means that shoppers arrived not just looking for the item they bought - they discovered it.
What is a self-driving store?
In a self-driving store, almost every aspect of shopper’s experience is individually tailored to the user. The Netflix homepage is a great example of such an approach:
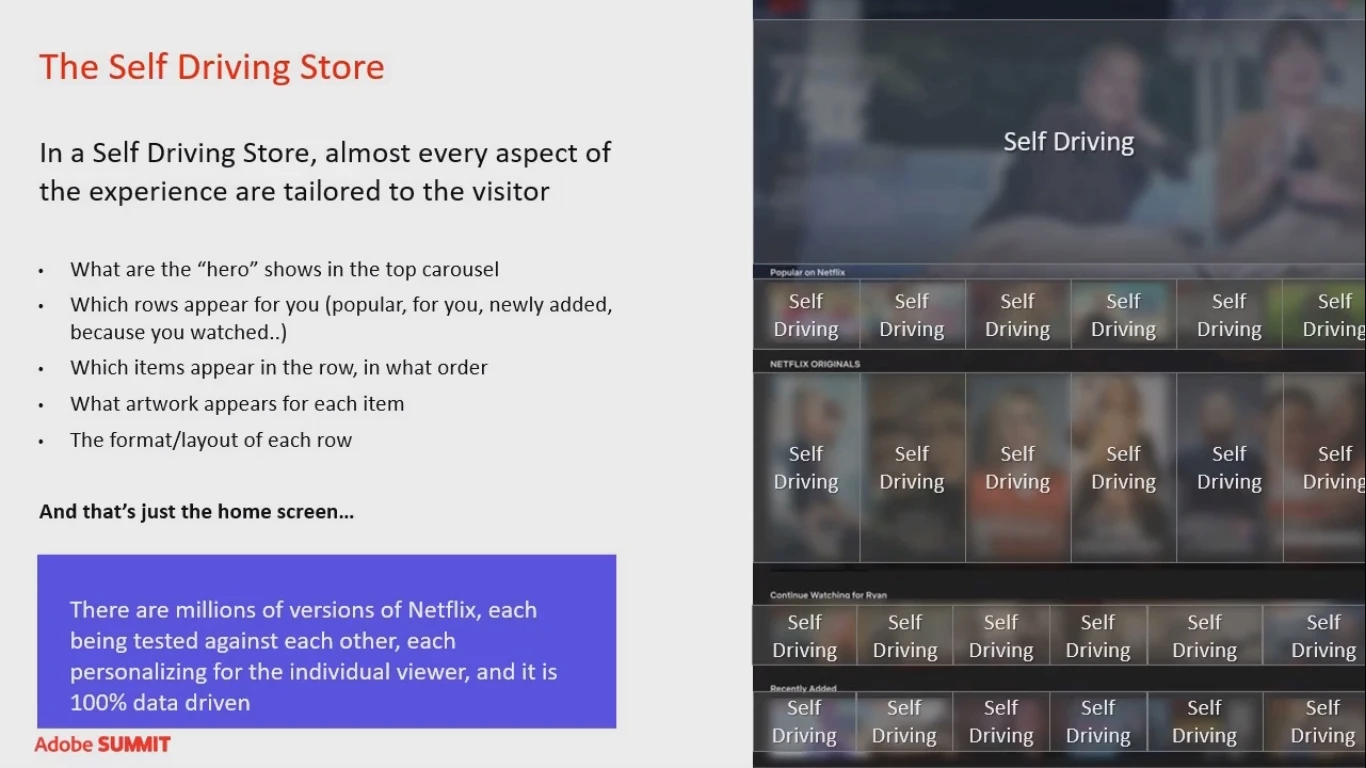
Almost every item on this page is tailored to a particular customer. For example, Netflix automatically generates different fan art for each title and learns what types of fan art the user likes more.
It is one hundred percent algorithmically controlled testing of millions of different versions to learn what creates the most engaging experience.
Opportunities for personalization
There is a wide variety of personalization touch points during the shopping journey, and most of them can be automated by making them self-driving.
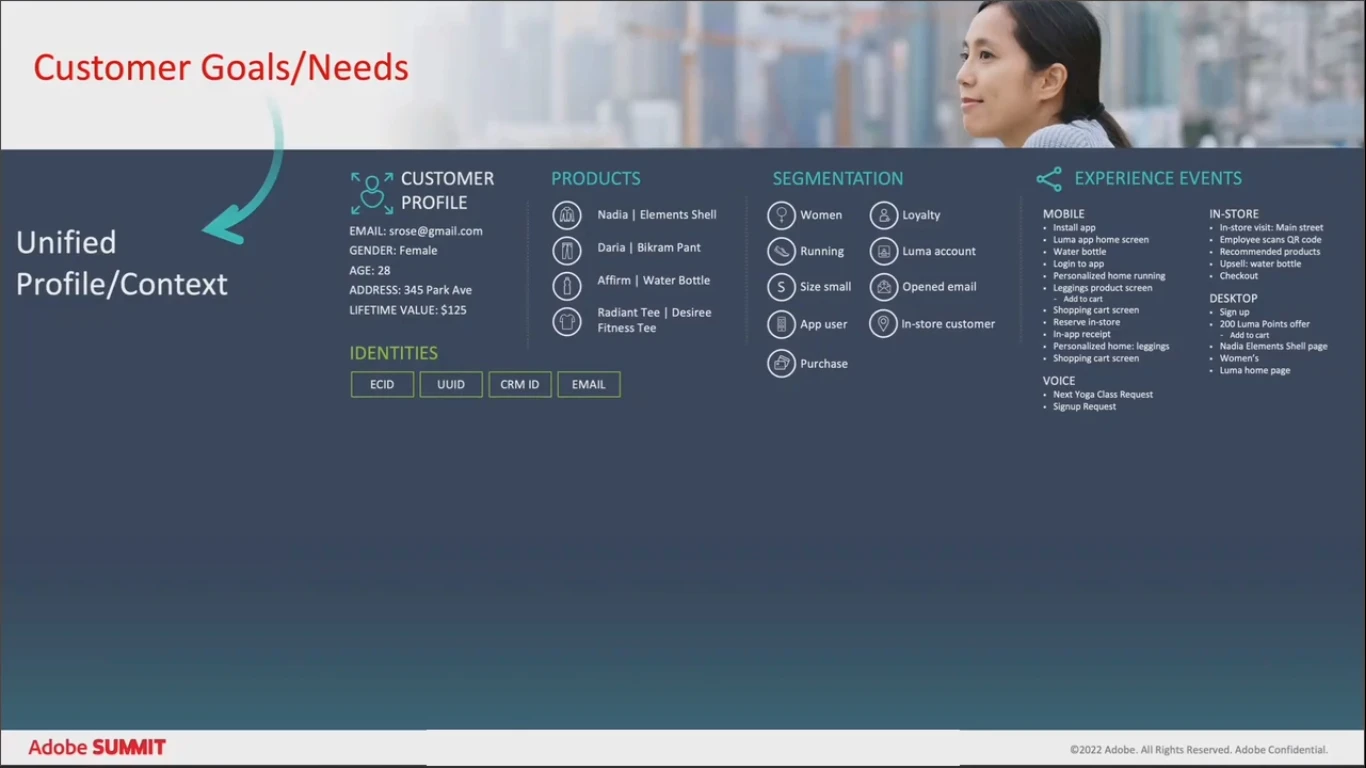
This level of personalization requires three things:
- A solid understanding of your business model, industry, customer goals, and needs;
- A unified data strategy. This means no more data silos, no separation of behavioral data across channels, online and offline data.
Example of AI self-driving the store
An example can help understand the concept of a self-driving store better, so meet a fictitious store named Luma Smart – a B2B and B2C merchant.
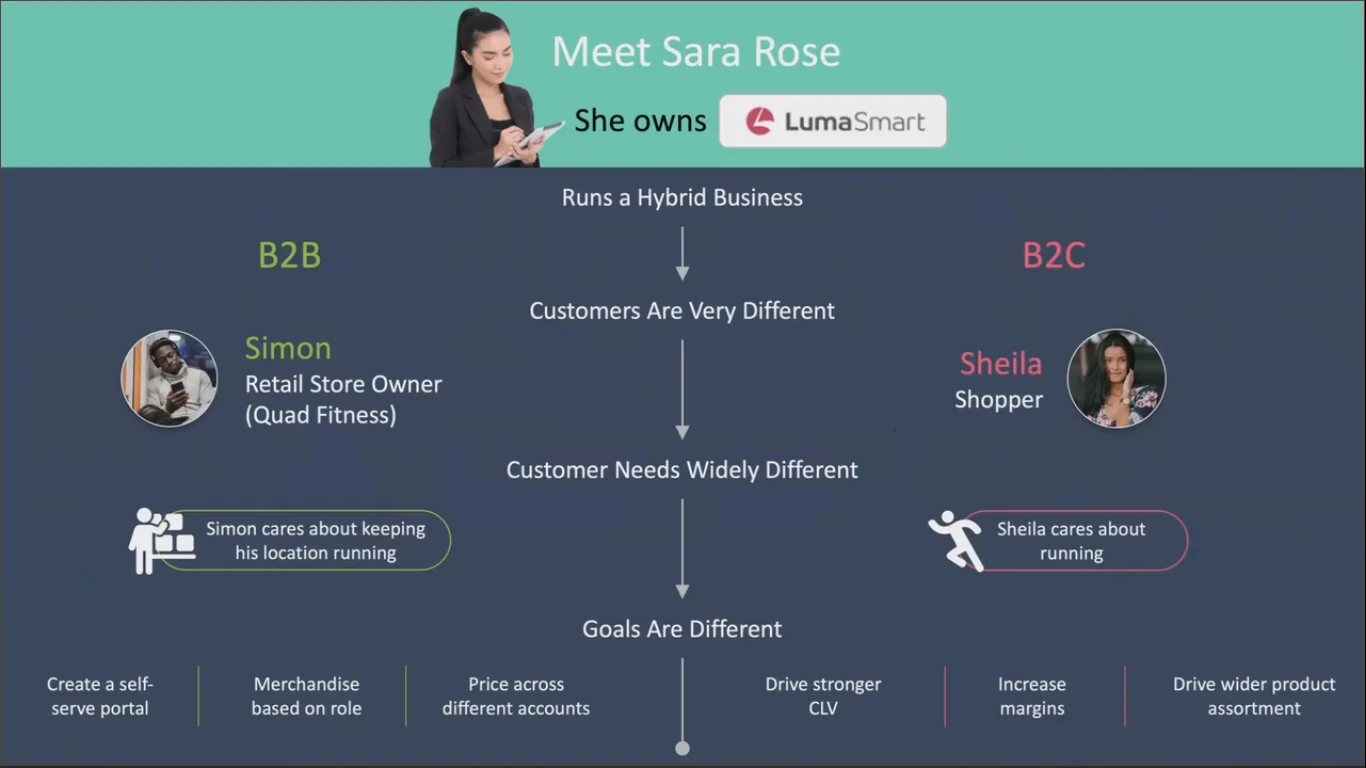
First, there is Simon, who owns his own boutique athletic retail store in the U. K. called Quad Fitness and gets inventory from Luma Smart. Simon makes a regular order every two weeks and also places orders as needed to replenish inventory.
Next, there is Sheila – an ordinary shopper in the U. S., who has made several purchases at Luma Smart.
Personalized B2C experience
Sheila typically lands on the Luma Smart home page, and its navigation items are tailored to Sheila’s preferences. This is especially useful on mobile responsive layouts where the number of navigation options visible is limited. This ensures Sheila sees the most relevant navigation options first.
Artificial intelligence uses Sheila’s preferences to select a banner to display on a store home page. The next item in the carousel is chosen based on Sheila's current context – the store knows that she is on the West Coast of the U. S. so this promotion is targeted based on that data.
Next, the store AI goes down the home page and fills the week carousel's deals. Typically it is manually created each week. But with AI, the store can decide what the most relevant deals to Sheila are.
Sheila is then presented with personalized product recommendations using collaborative filtering algorithms. They show Sheila which items people like her are most interested in real time. Algorithms can also filter the items in stock and available at a store near her.
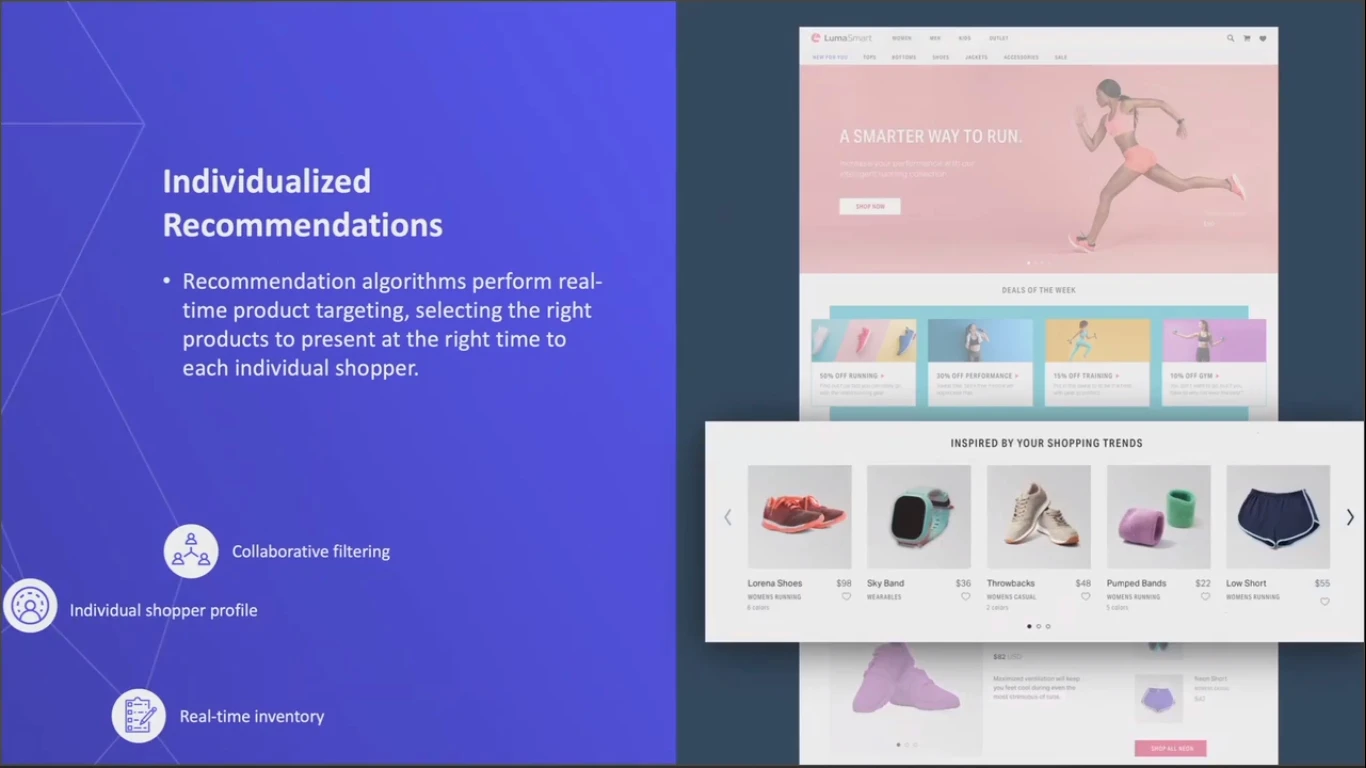
Having a great search experience is key for any commerce site in a self-driving store. Intelligent search can provide relevant zero query results before the shopper even starts typing. Understanding the shopper’s intent and the meaning of queries is done using natural language processing.
Personalized B2B experience
Simon's B2B buying experience is different but equally supercharged by data and AI.
Instead of personalized recommendations for him, they become individualized recommendations for the store. Instead of zero content highlighting products or promotions for him, the page can be tailored to the content for the store and sales staff.
Simon also sees suggestions to help B2B buyers in assortment planning and consider what additional items they should consider adding to the store catalog.
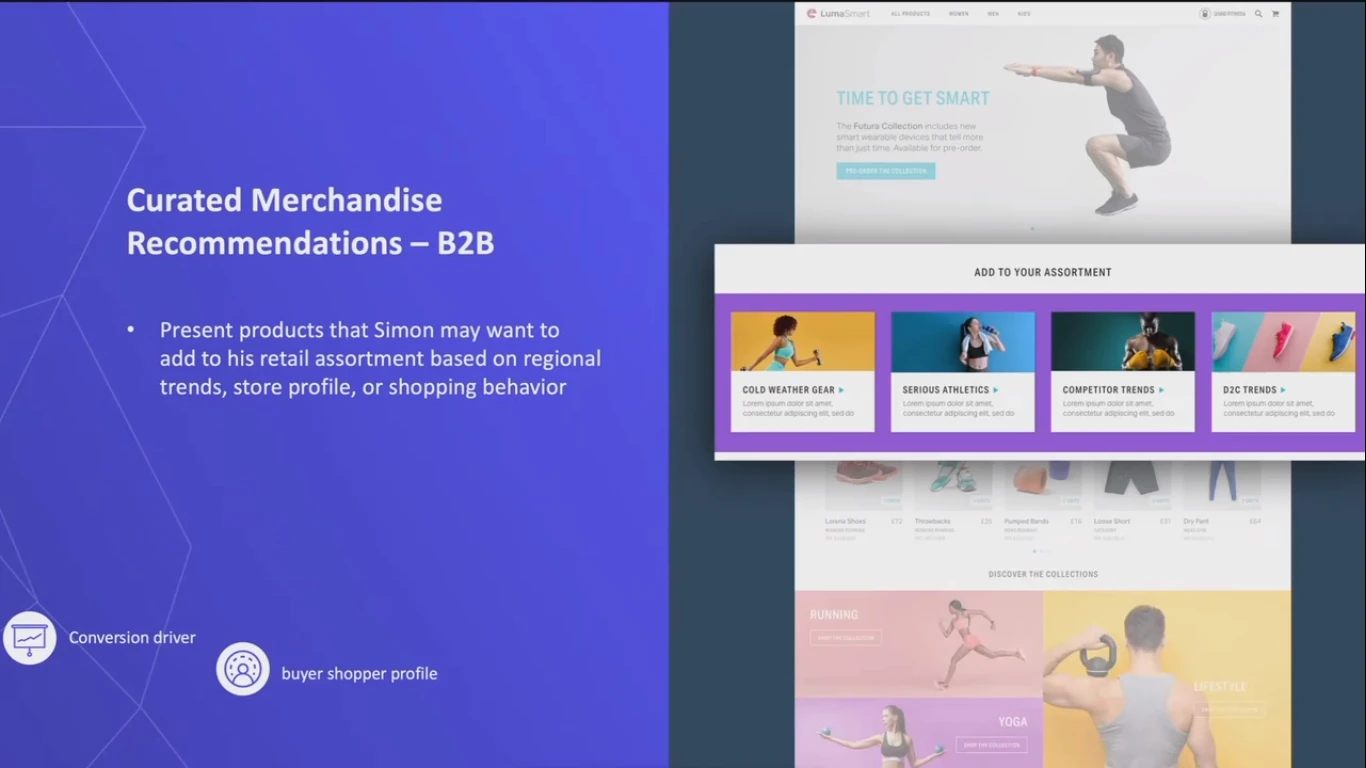
In this way, Simon also gets hyper-personalized experiences with content presented to him that is individually relevant to him and the needs of his store.
Automating product positions
Merchants still need an individual level of control to boost or bury certain products in categories based on the store’s business needs. Smart search dicing lets merchants create dynamic rules for which products or categories to promote.
The level of detail presented can also be personalized in a self-driving store. The algorithm predicts whether this is a shopper who is likely to want details or just a summary of the product.
Using shopping basket analysis algorithms, a store can create bundles suggestions. If it turns out a product is not right to the shopper, our self-driving store can recommend other products that he or she might be interested in using collaborative filtering algorithms.
Self-driving store goes beyond the web store
The relationship doesn't stop at the checkout. The store takes care of the post-purchase phase.
For example, it sends educational materials for the B2B clients, or it may remind them to restock products or bring in seasonal inventory. B2C clients also get post-purchase treatment, which can be tips on using the purchased product.
Self-driving stores are the near future
Adobe’s expert said that self-driving stores' future is not that far off. Today, many AI-powered experiences are available directly in Adobe Commerce and Adobe Experience Cloud.
Adobe Commerce comes out of the box with Adobe Sensei powered features such as product recommendations for B2B and B2C, and live search for intelligent search capabilities.
Adobe target brings advanced segmentation and optimization to pick the right experience for the right person at the right time. Customer journey analytics gives insights into how your shoppers are behaving, what's working, what's not, and even spot unexpected changes in metrics and identify the causes of those changes.
Adobe journey optimizer continues journey optimization across touchpoints even after your customers leave the site.
How to begin transitioning to a self-driving store
If you want your store to be more self-driving, you can start by identifying the low-hanging fruit. For example, features like product recommendations on live search could be the key in AI-powered features with a huge impact.
Merchants observe average order value from product recommendations and conversion rate increase up to15% after turning on live search.
Next, you want to break down data silos. A single unified view of your customers and visitors across different touchpoints in channels is required, so you don't miss an opportunity to make interaction personal. Real-time customer data platforms can bring customer data together across channels.
Finally, you need to be able to activate data and profiles across channels for true omnichannel personalization. To do this, you need to have a unified data strategy, and the data needs to be accessible across channels.
Top CMS Innovations
Product management experts in Adobe Experience Managers Sites Haresh Kumar and Cedrik Husler presented top innovations in content management systems.
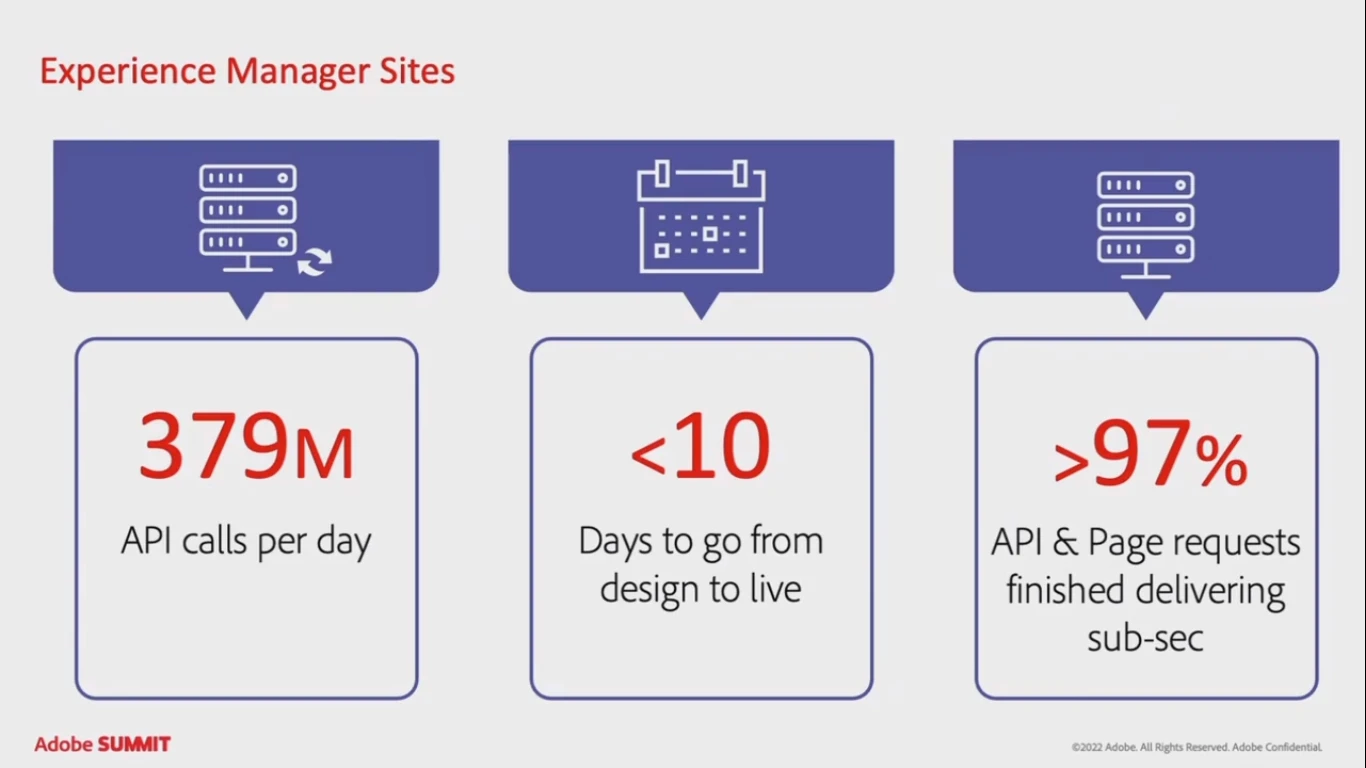
The Adobe Experience Managers Sites (AEM) is a tool for stores to create and deploy personalized experiences. The popularity of this tool is on the rise compared to the traditional way of content delivery through HTML pages. Partly it is because of the easiness of usage and work speed.
New workflow for frontend developers
The Quick Site creation technology builds a website more easily, and the work can be started from a template. Installing components – themes, templates, sample content – is done in the background.
Customization of the site’s visual appearance can be done through Theme Sources. It has everything a frontend needs to do the job. Additionally, files for designers can be downloaded.
Changes can be viewed locally to preview the changed visual style. After finishing, the code can be deployed to the site frontend in a few minutes.
Adobe’s experts consider AEM as a new workflow for front-enders that minimizes the number of steps before they can start working.
Simple analytics integration
The analytics integration usually takes place in several stages. The Adobe Experience Manager simplifies it to a few clicks: select the site, and click on the analytics integration button.
The site owner has to answer one question – how they want to call the integration. Data collection, UI, data mapping and other stuff is done behind the scene automatically.
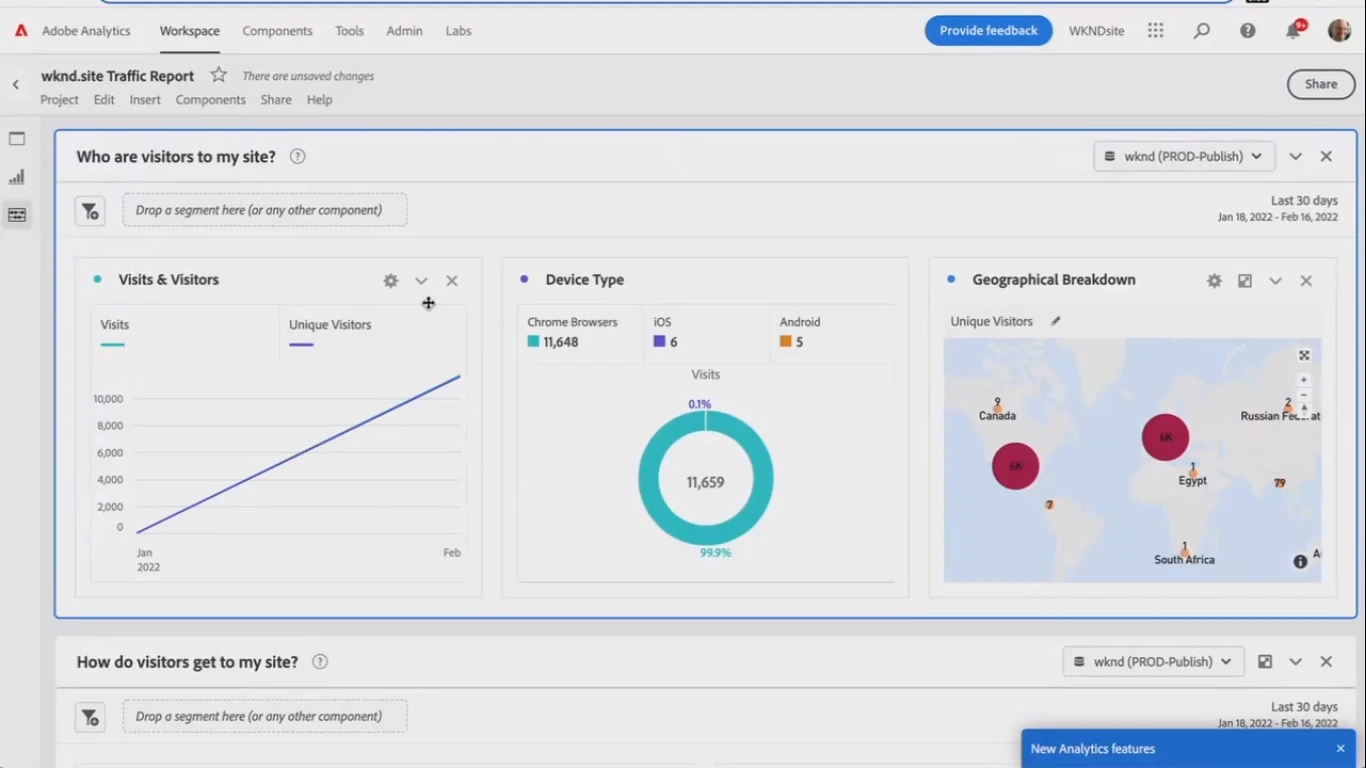
At the end, the site owner receives a detailed report with data about where users came from, what they did, which pages were best, etc. The report tracks each component present on the page.
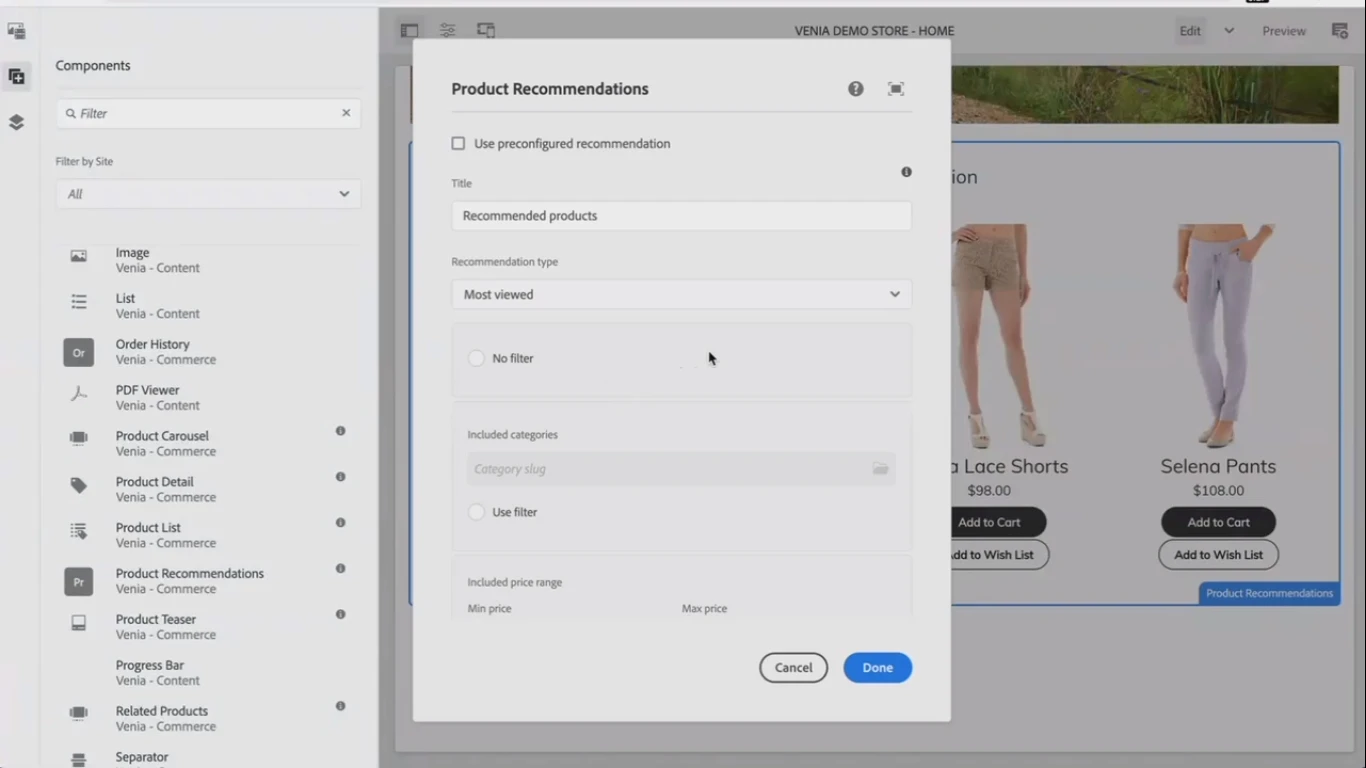
Personalization technologies
Personal experience is key, and AEM allows getting the most from using this approach with several ideas.
The first idea – is the capability to simulate a scenario by switching between different personas to see how the content is changing. Experience fragments allow creating content variations and managing them in one place.
Product recommendations can also be innovated by integrating AEM. The recommendations in the Magento system can be brought to AEM.
Speed and performance
While working on functionality, the AEM developers also kept in mind the speed. Therefore, customers can get high-performance scores from Google Core Web Vitals out of the box.
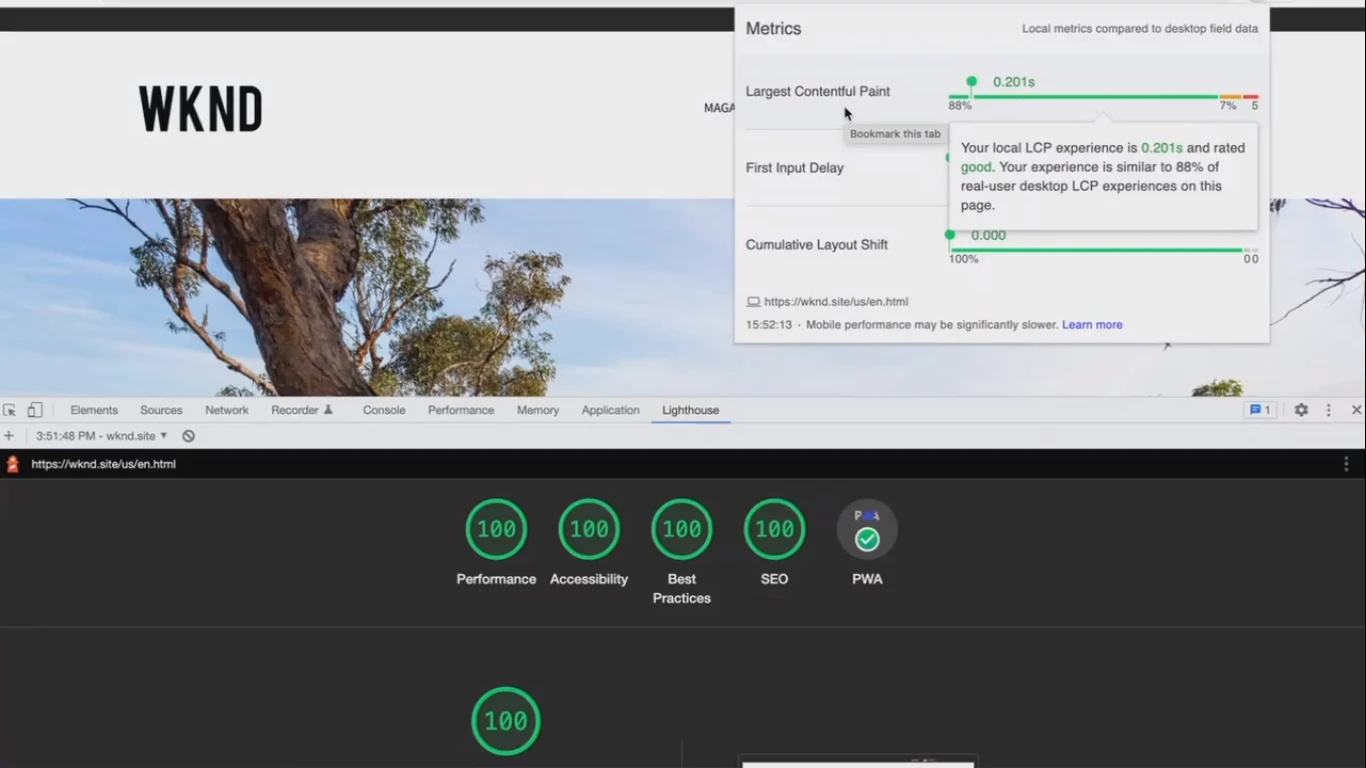
AEM developers are particularly proud of how they managed to speed up image delivery, especially on mobile. CDN is a key part of faster delivery, and AEM can handle significant traffic volumes thanks to tight integration with CDN.
In the middle of the year, the CMS will also get a new UI to manage content fragments to further increase the site performance.
B2B marketing automation in 2022
Venu Tavisals - the head of Adobe Marketo Engage product – unveils innovations coming for B2B marketing automation in 2022. It includes new ways to drive marketing efficiency, scale, and impact, new channels for marketing and sales to engage with customers.

Adobe Marketo Engage is a toolkit to deliver lead-based and account-based marketing. Its efficiency speaks for itself:
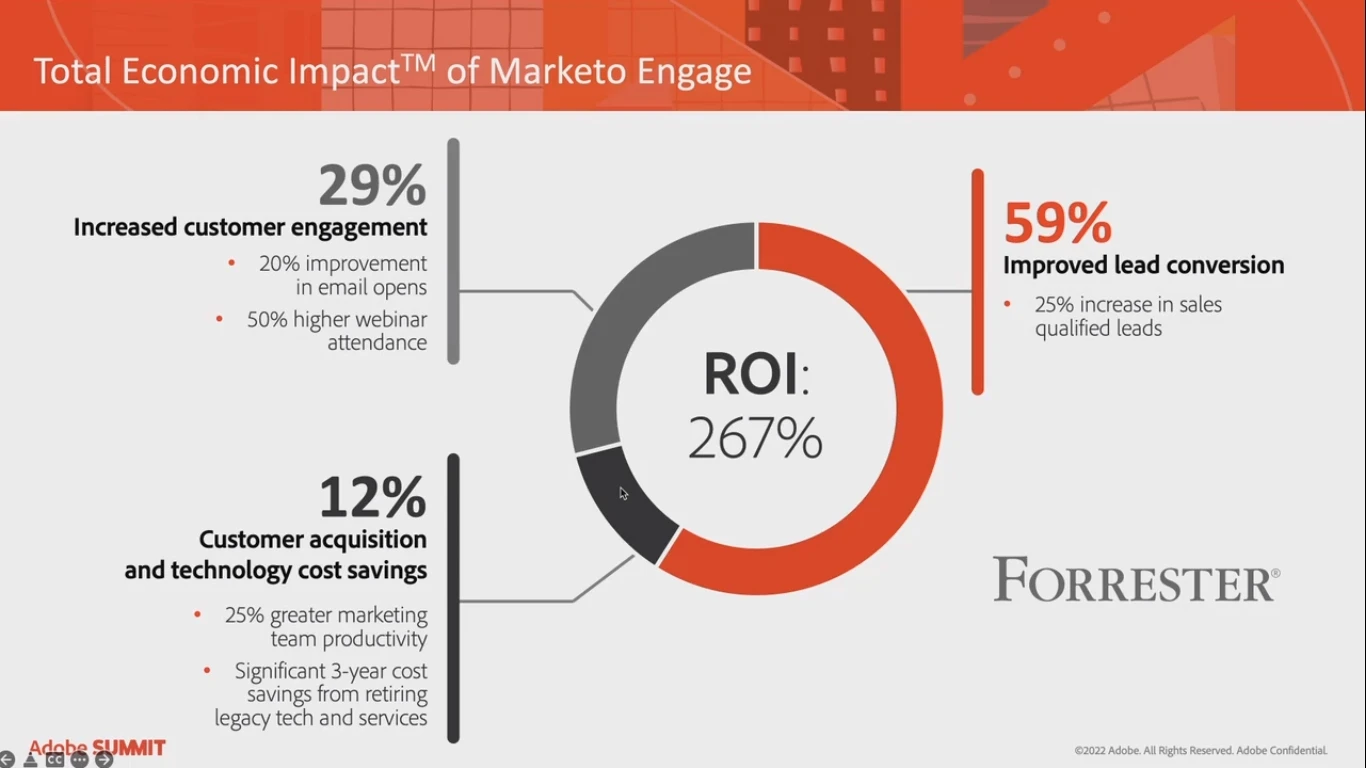
To further increase online business results, Marketo Engage offers its vision, which is based on automation.
Marketo Engage will offer to combine all its instances into one data platform to obtain unified profiles for B2B marketing.
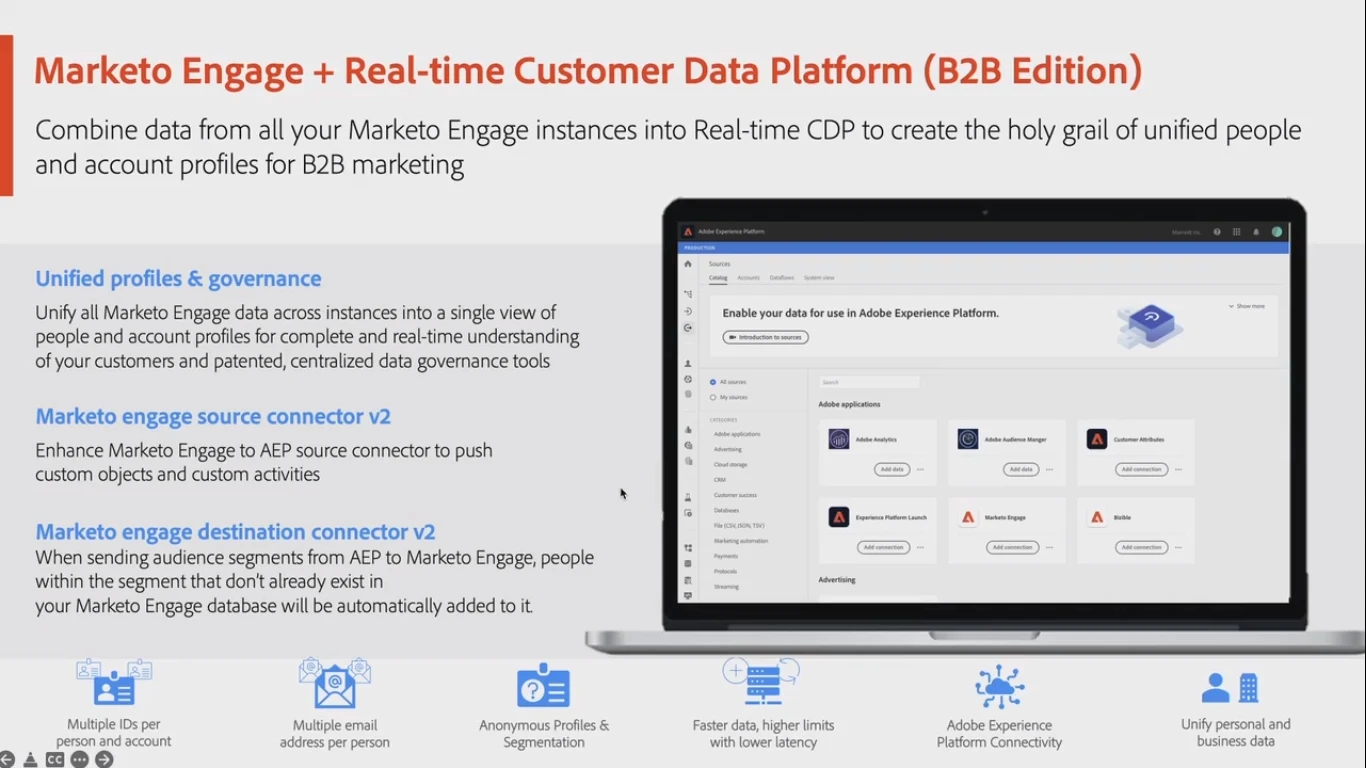
Users of several Adobe Experience Cloud products will be able to use them through a single account instead of several ones as it is required now. This streamlines user administration across Adobe’s cloud products. Existing customers will migrate to the updated system in the second half of 2022.
Predictive lead and account scoring
Businesses will get a tool to engage with their customers at the right time more easily. Artificial intelligence (AI) eliminates the rules for scoring models leading to higher accuracy and faster time-to-value.
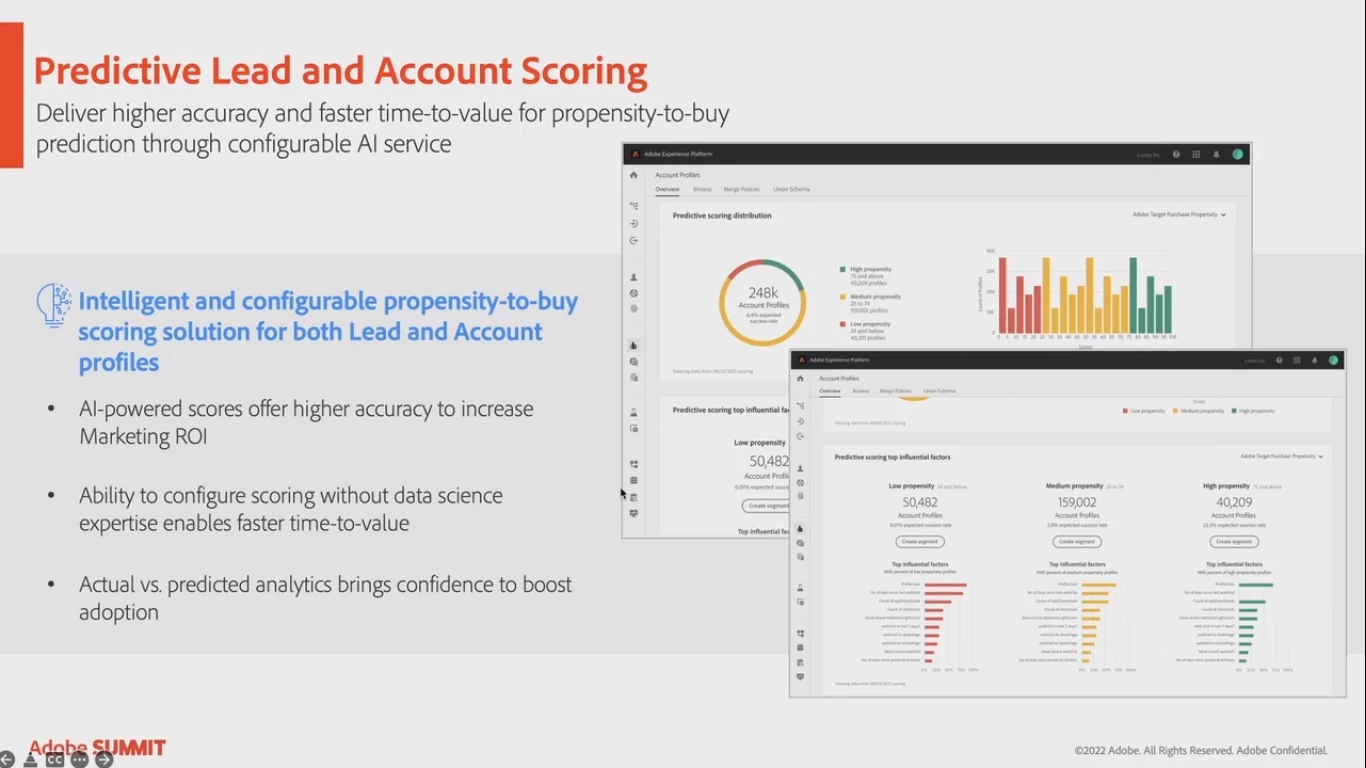
The AI can be configured without having profound expertise in data science. Still, businesses will receive a clear scoring explanation that, in the end, will speed up the adoption of this system.
Lastly, businesses will get actual and prediction reports to verify that boost confidence in the accuracy of the prediction models.
Predictive lead and scoring will become available in the second half of 2022, first for B2B and B2P platform users and then will be rolled for the rest of the Marketo Engage customers.
Innovation for experience
Marketo Engage will offer a Dynamic Chat approach for leveraging real-time communication. This allows generating more qualified leads for the business.
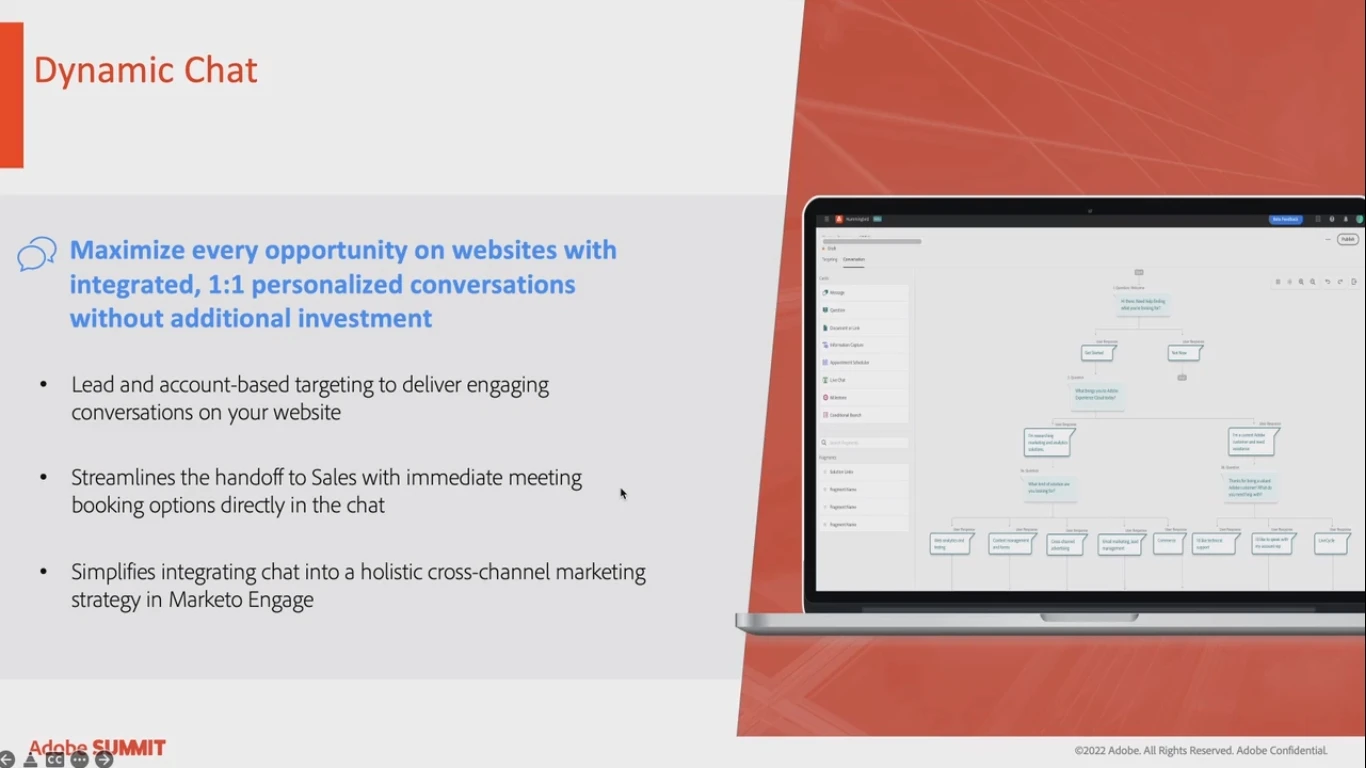
This functionality will be available for all clients as a part of the standard offering.
Additionally, it receives conditional branching, starter templates, targeting based on Marketo data.
How to use Log Forwarding to monitor your Compute Worker
You are a customer of Adobe Experience Manager, and your team created Custom Asset Compute Worker for watermark adding. How to debug issues with this custom app?
Manik Jindal, Product Manager, Adobe Developer Console at Adobe and Olga Kopylova, Sr. Architect at Adobe, explain how to use Log Forwarding in App Builder application to better monitor the application’s health.

Let's say the Custom Asset Compute Worker sometimes outputs wrong watermarks or they are not generated at all.
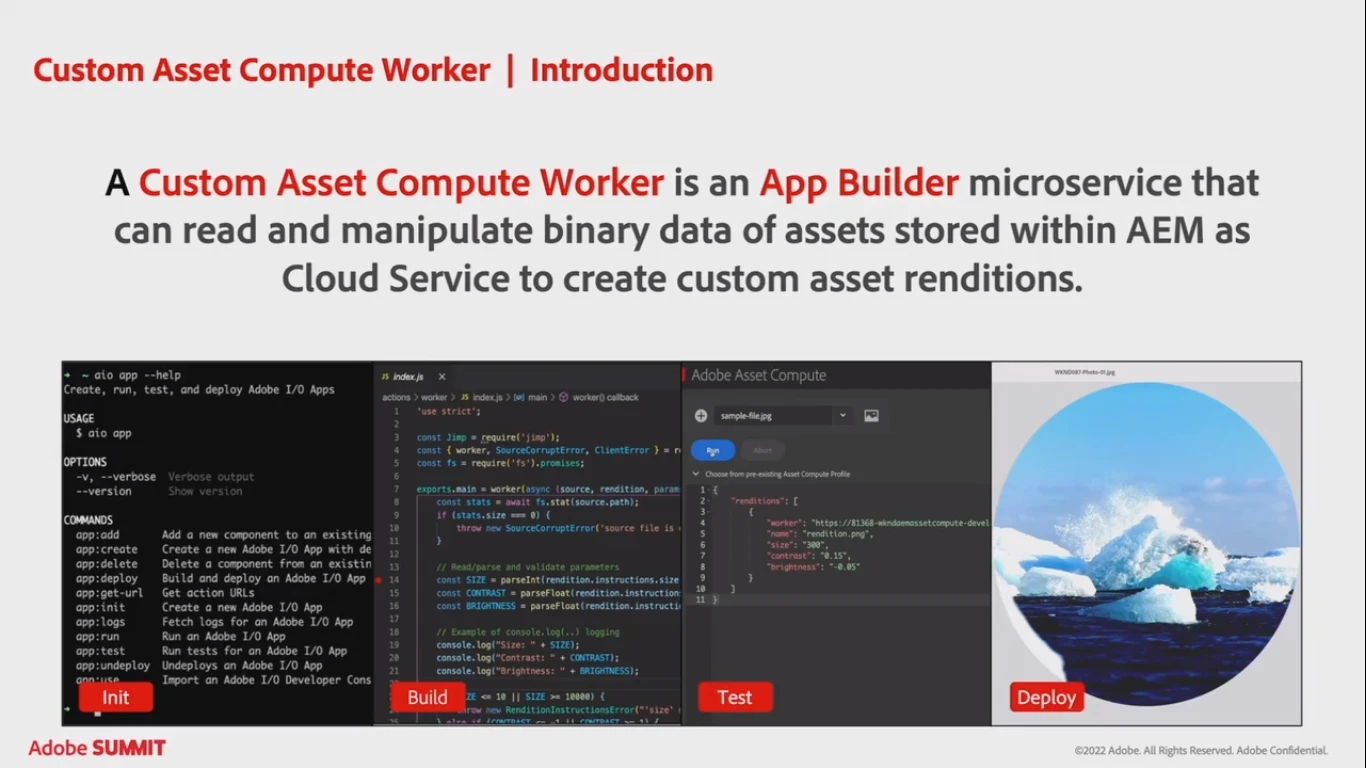
Each Compute Worker is a microservice that can log information using the console.log function. Any such log by default is stored by Adobe I/O runtime and can be fetched using command-line tools:

Custom Worker debugging in production
In production, thousands of assets can be uploaded simultaneously, generating multiple lines of logs. The Adobe App Builder capability of log forwarding can be used to filter out irrelevant logs with customer’s log observation solution.
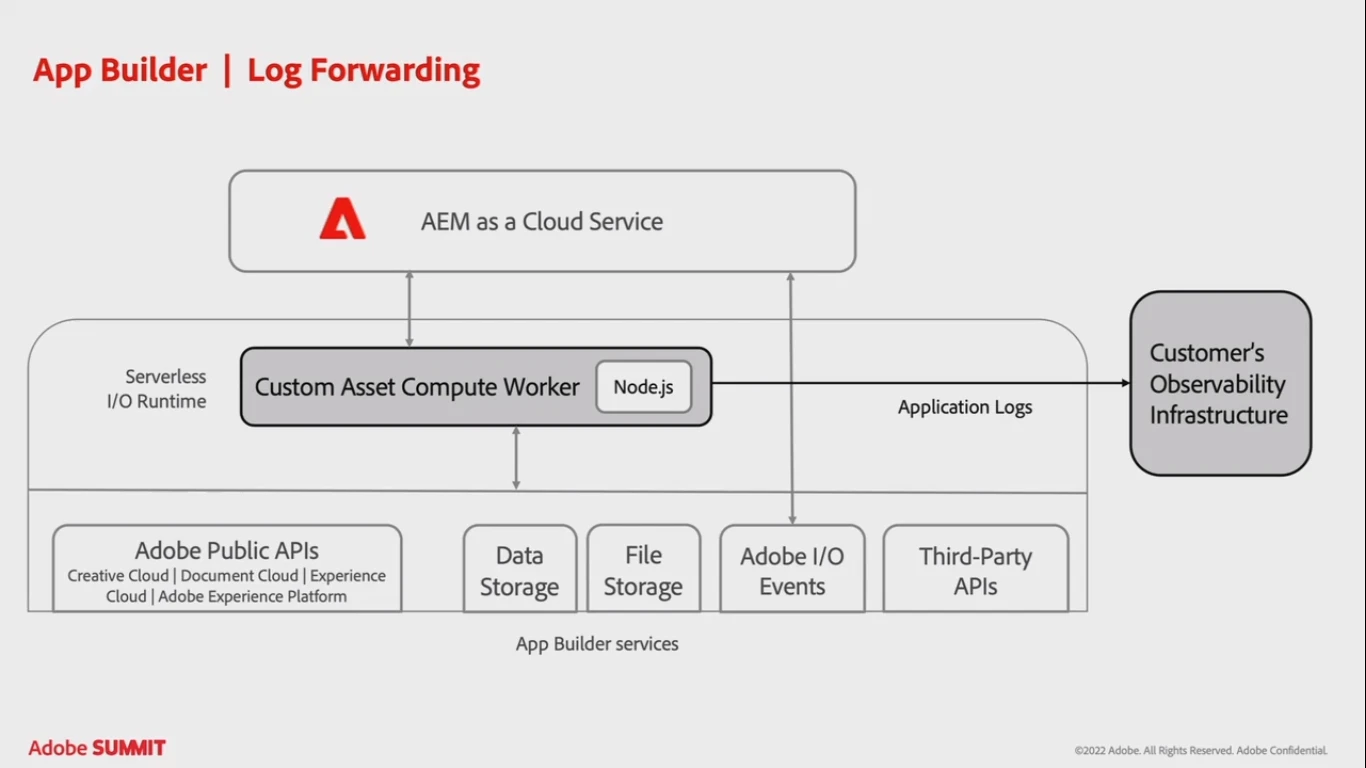
The benefits of log forwarding can be categorized as:
- access to all logs. Developers can access all App Builder logs and control the log retention period;
- search in logs. Search in logs, set alerts, visualize logs;
- logs consolidation. Logs can be consolidated within the observability infrastructure, streamlining the situation response.
The log forwarding functionality is supported with such solutions:

Log forwarding demo
The demo goes through the scenario in Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) where a developer works with assets. The task is to generate a special rendition with custom logic. The output should be an original image with a logo applied on top as a watermark.
The first step is to create an Asset Compute Worker with this custom logic, integrate it with AEM, and configure demo folders for assets.
The worker with its logic will look like the following:
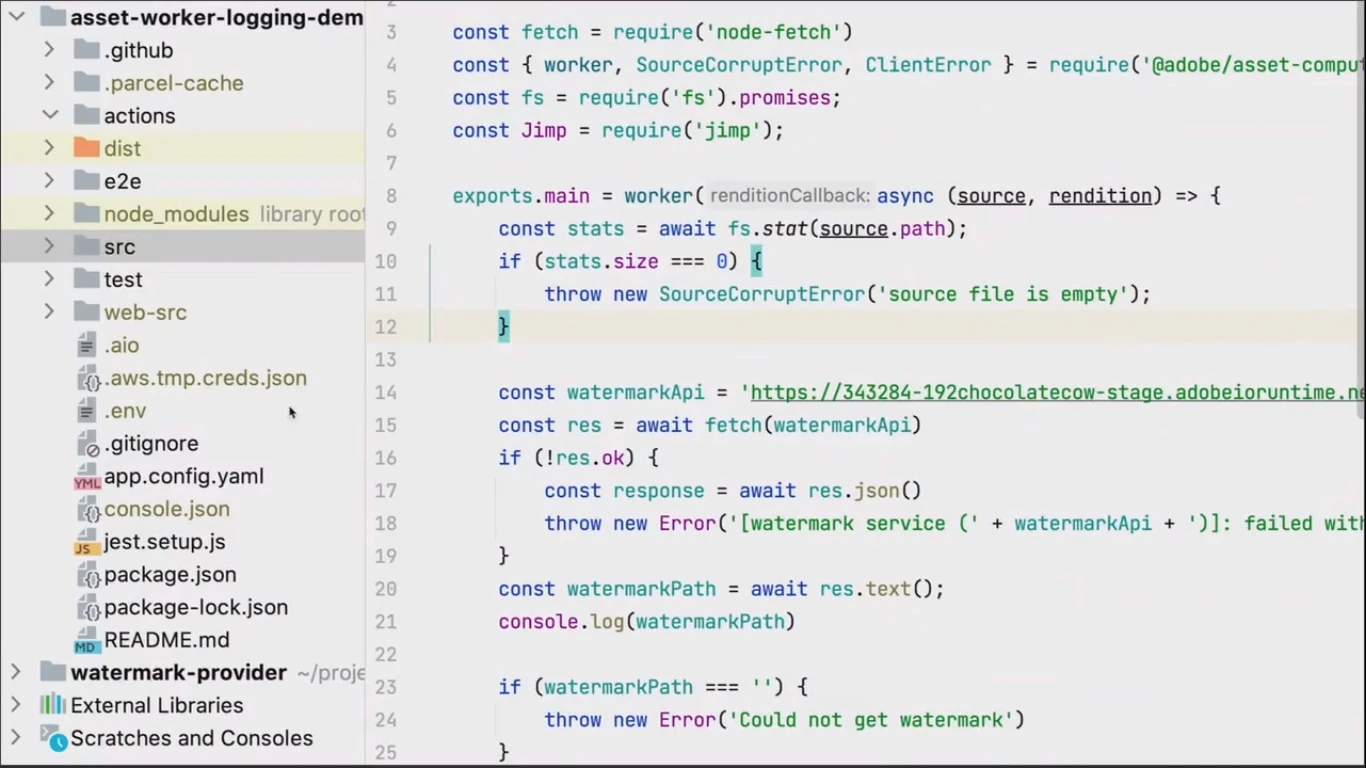
The worker communicates with external service, which provides watermarking functionality.
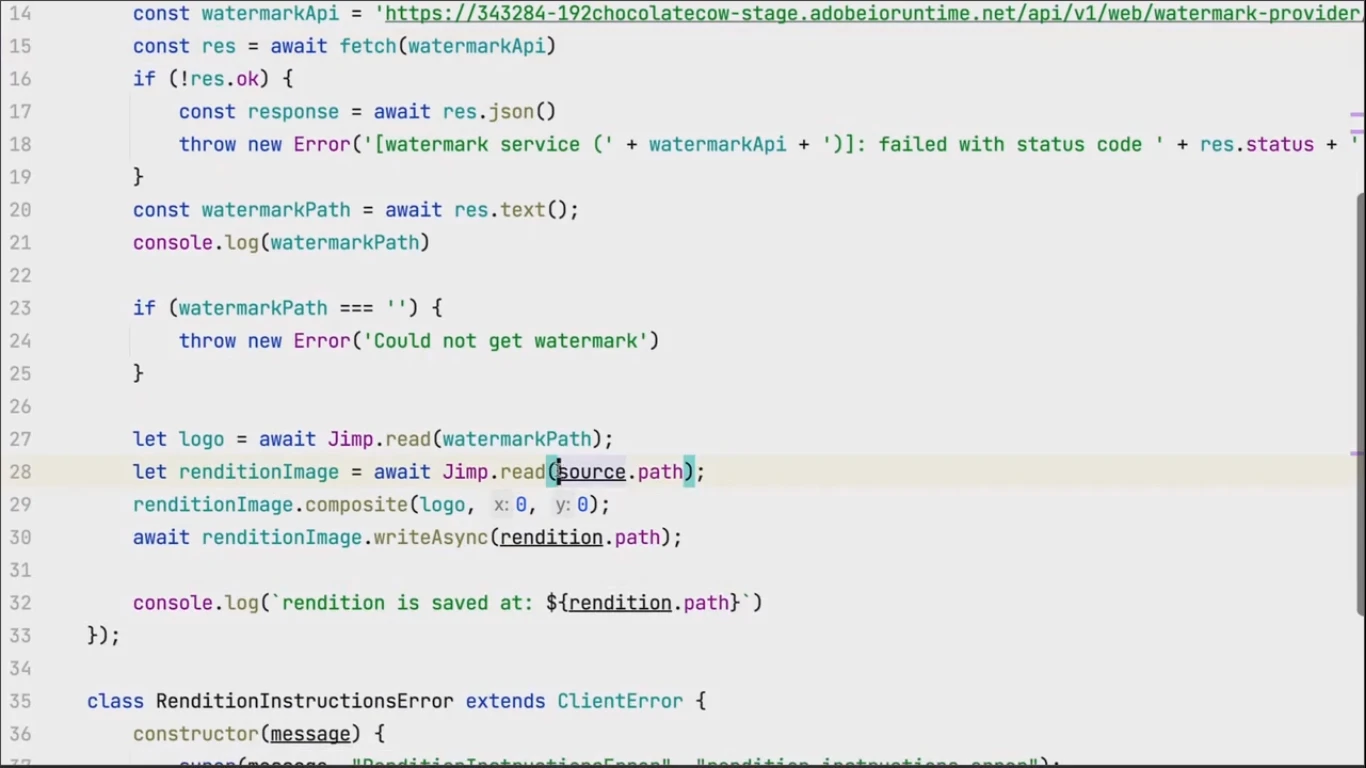
The watermark is then combined with the original image and stored in a rendition.
Launch the log monitoring to debug the Compute Worker with command aio rt activation logs. An error message with problem explanation can be found (Worker reached the watermark quota of external watermarking service):
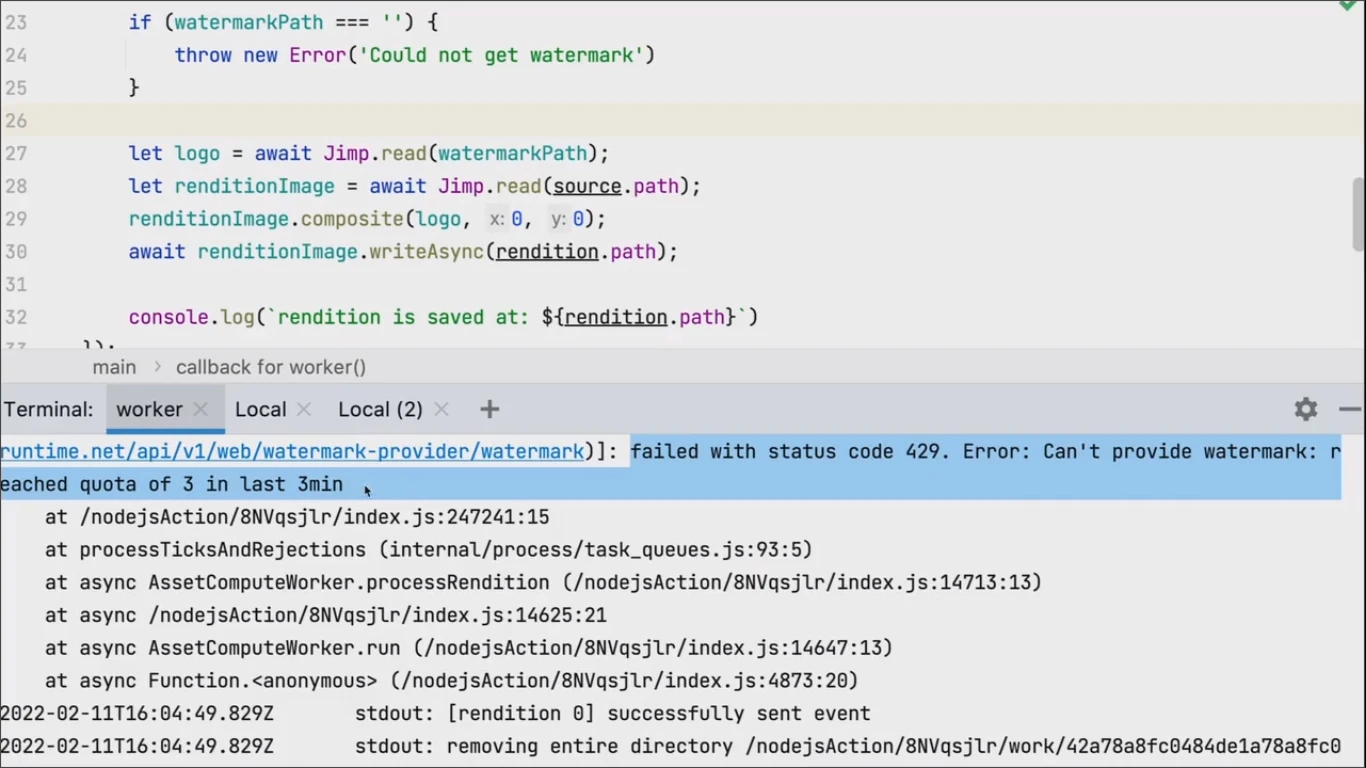
Using Log Forwarding
Use the command aio app config set log-forwarding to configure log forwarding to an external observation system.
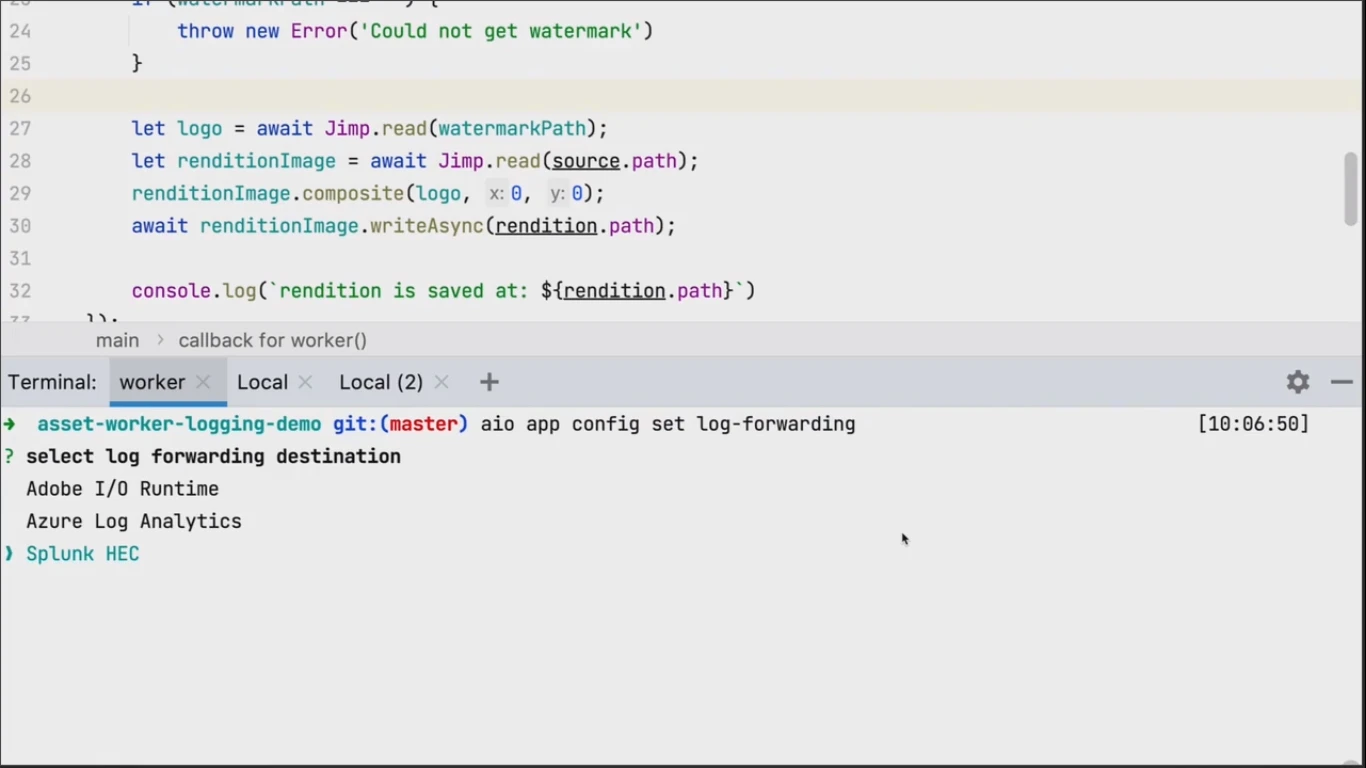
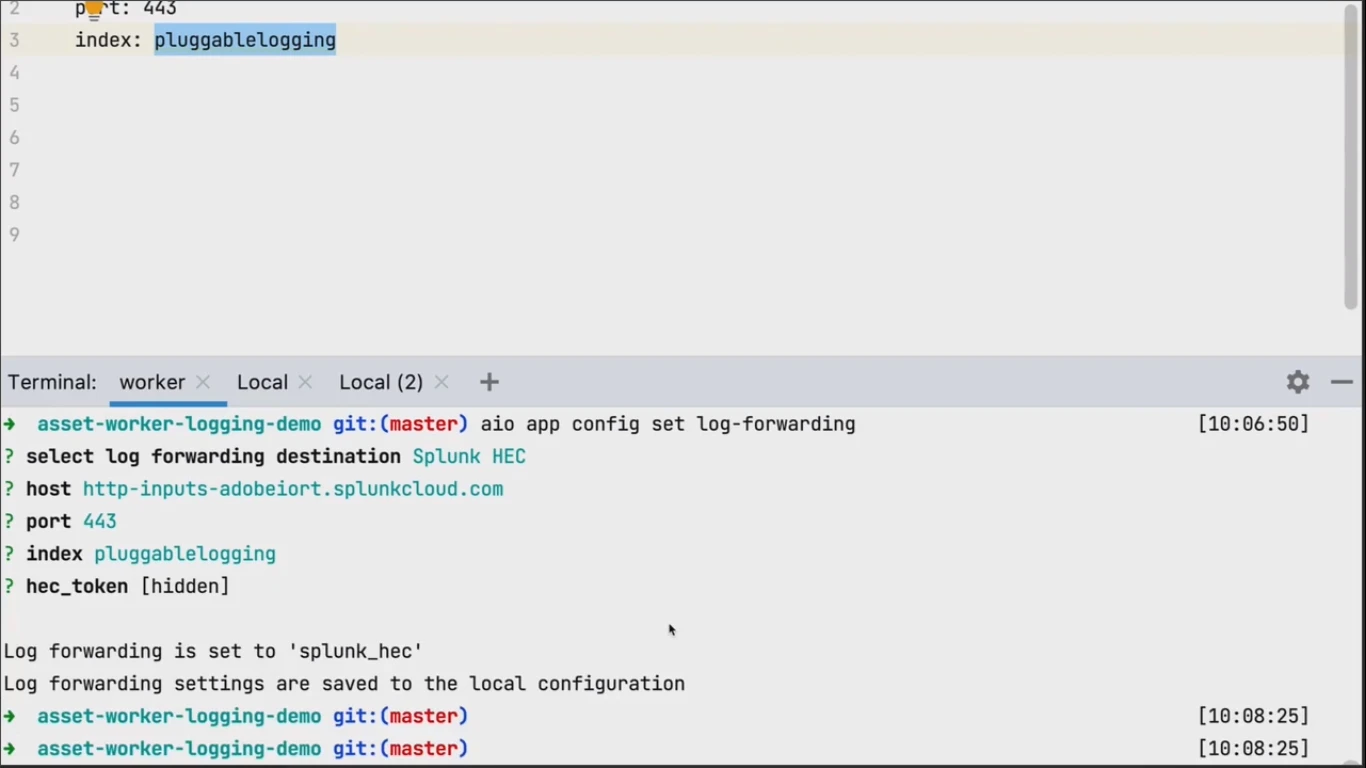
Simply select one of three available systems. For this demo it is Splunk. Provide required arguments for connecting to your Splunk instance:
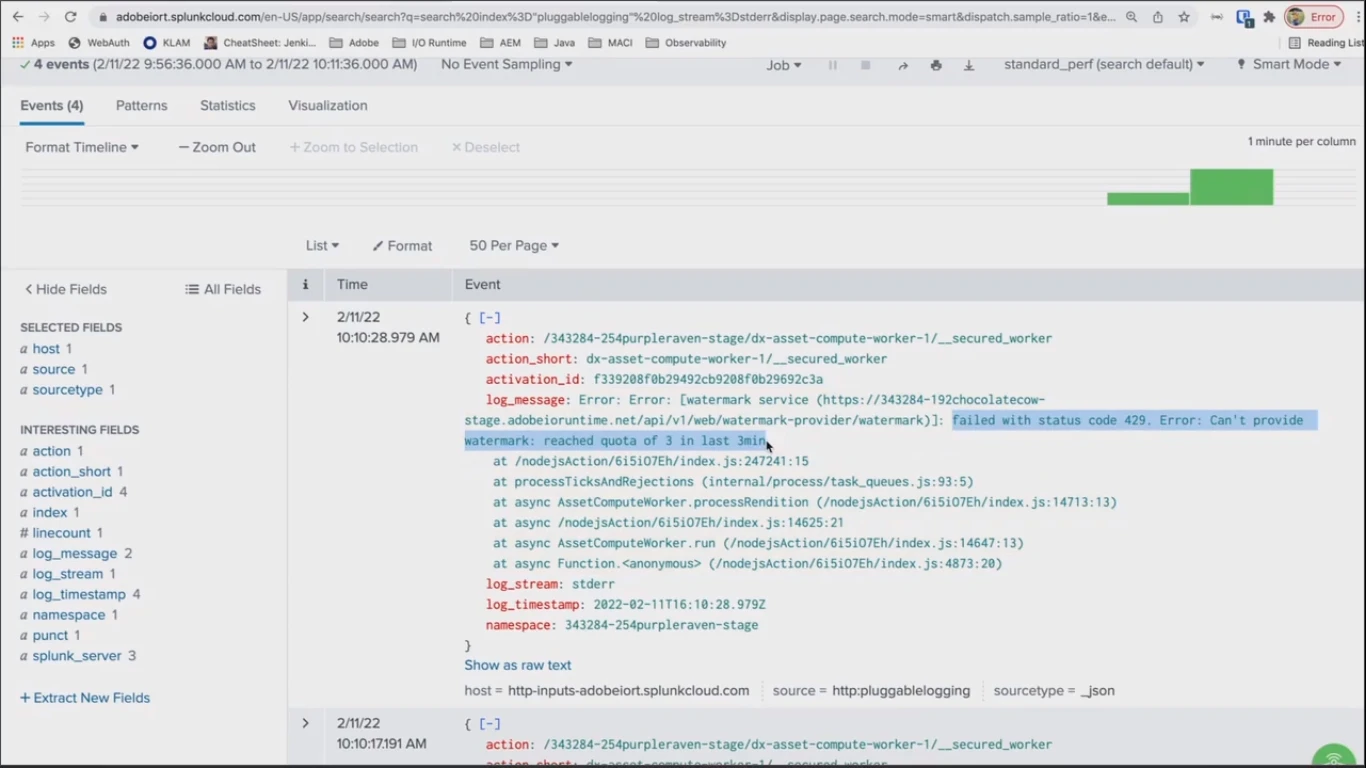
Using filtering capabilities of the centralized log managing tool like Splunk, it becomes easy to find the error on production projects:
 Read more on Log Forwarding on tinyurl.com/appbuilder-setup-logforwarding.
Read more on Log Forwarding on tinyurl.com/appbuilder-setup-logforwarding.
Summary
Adobe Summit is an event where anyone can learn from executives and engineers who work at Adobe and big online stores. They share how customer experiences are the currency of the digital economy and how business owners can excel in building personalized customer experiences.
This event allows you to take a peek at potential future technologies in the eCommerce world and get useful lifehacks for your store infrastructure.




